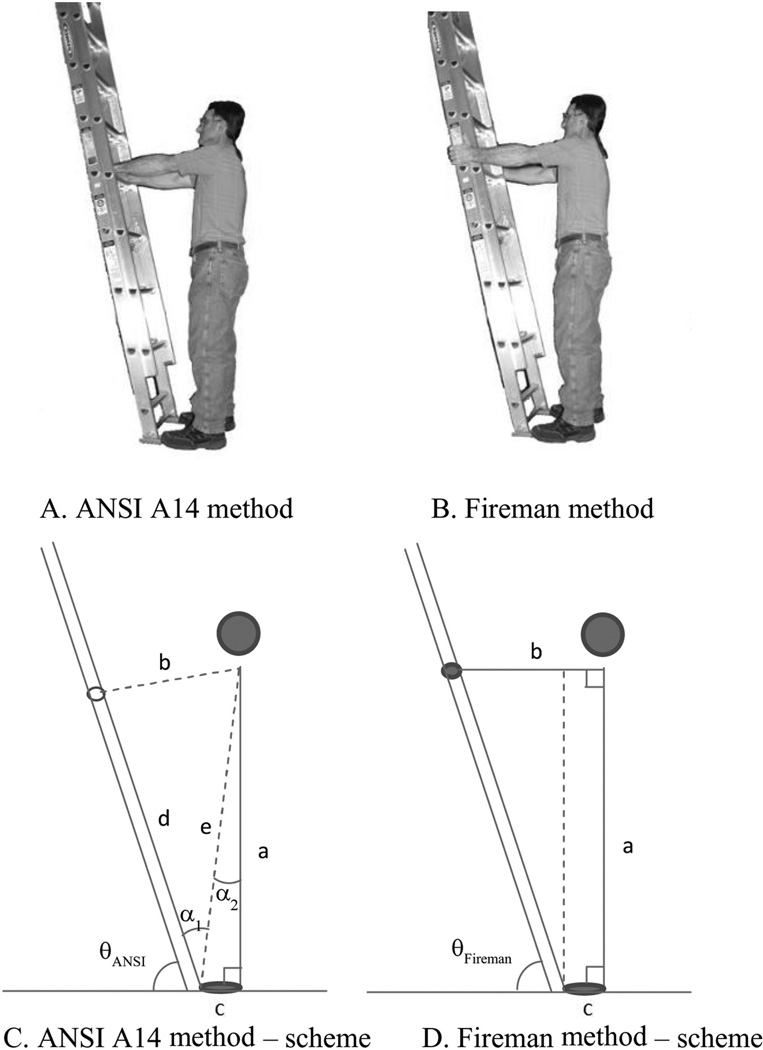
Figure 2.
The two anthropometric methods for ladder positioning and their schematic geometrical representation. (A) ANSI A14 method. (B) Fireman method. (C) ANSI A14 method scheme. (D) Fireman method scheme. θANSI = 90° − α1 + α2 = 90° − arcos[(d2 + e2 − b2)/(2*d*e)] + arctan(c/a), and θFireman = 90° − arctan[(b − c)/a)], where a = shoulder (acromial) height in standing (with shoes), b = grip reach from shoulder (reduced by half of the ladder rail width), c = ankle-to-toe length (average of medial and lateral measurements with shoes), d = length from ladder bottom to fifth rung, and e = (a2 + c2)0.5.