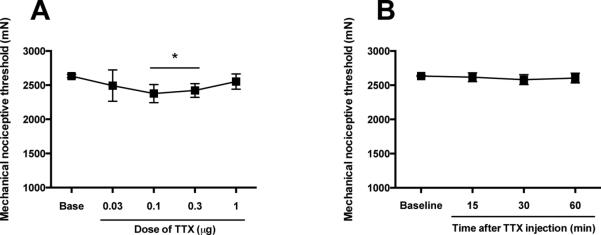
Figure 1. Effect of intramuscular TTX on mechanical nociceptive threshold in naïve rats.
(A) Sequentially increasing the i.m. doses of TTX, each cumulative dose one-half log unit greater than the previous dose, were injected at 45 min inter-injection intervals. Prior to each subsequent dose, the mechanical nociceptive threshold was again assessed. TTX failed to produce an increase in mechanical nociceptive threshold in normal control rats at any of the tested doses. Indeed, the doses of 0.1 and 0.3 μg produced a small, albeit significant, decrease in mechanical nociceptive threshold. (B) In a separate group of rats, the injection of the highest dose of TTX (1 μg) did not modify the mechanical nociceptive threshold up to 60 min after injection. *P < 0.05.