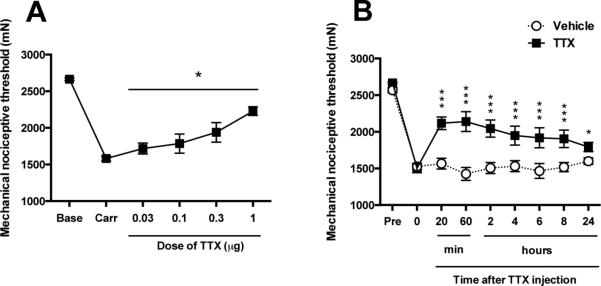
Figure 2. Effect of intramuscular TTX on inflammatory mechanical hyperalgesia.
(A) The injection of λ-carrageenan (100 μg/10 μl) into the gastrocnemius muscle produced a decrease of mechanical nociceptive threshold (Carr) measured 24 h later. At this time point sequentially increasing doses of TTX, each one-half log unit greater than the previous dose, were injected at 45 min inter-injection intervals. Prior to the injection of each higher dose of TTX, the mechanical nociceptive threshold was again assessed, to determine the effect of that dose on the carrageenan-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. TTX produced a dose-dependent increase in mechanical nociceptive threshold, in the presence of carrageenan induced mechanical hyperalgesia. Of note, not even the highest dose elevated the mechanical nociceptive threshold above the pre-carrageenan baseline. (B) After the highest intramuscular dose of TTX, or vehicle, were injected the mechanical nociceptive threshold was monitored to evaluate time course of their antihyperalgesic effect. Compared to vehicle, TTX induced a significant increase in mechanical nociceptive threshold, reversal of hyperalgesia, up to twenty-four hours after the local injection of a 1 μg dose of TTX, in carrageenan-injected rats. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.