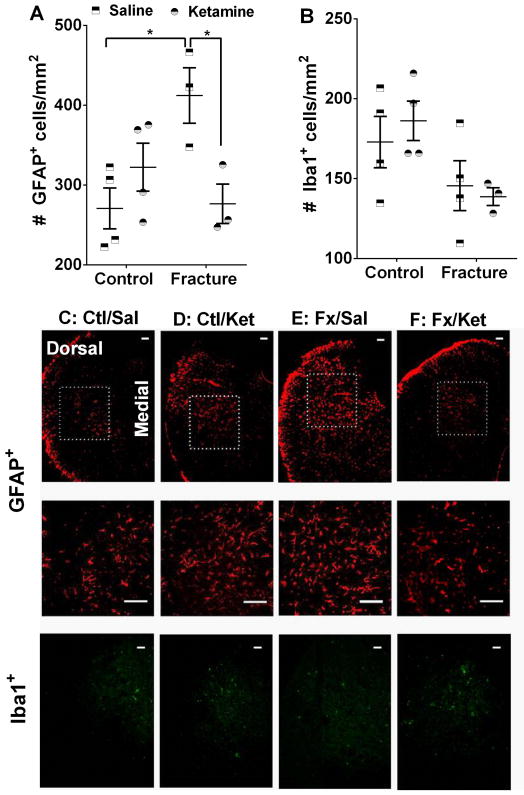
Fig. 7. Ketamine exposure ameliorates complex regional pain syndrome-related upregulation of spinal astrocytes.
Immunohistochemical staining for GFAP shows that, in comparison with control animals, fracture mice exhibit increased numbers of astrocytes in the dorsal horn of the ipsilateral spinal cord 10 weeks after fracture. This increase is absent in the ketamine treated group (A). In contrast, no changes were seen in the number of Iba1+ cells at this timepoint (B). Examples of GFAP- and Iba1-stained sections are included in panels C–F. The areas enclosed by the dotted squares are further enlarged in the central panels. Scale bar = 100 μm *p<0.05. Sample sizes are shown in the scatter graph. GFAP= Glial fibrillary acidic protein, Iba1= Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1, Ctl/Sal=Control + Saline, Ctl/Ket= Control + Ketamine, Fx/Sal= Fracture + Saline, Fx/Ket= Fracture + Ketamine.