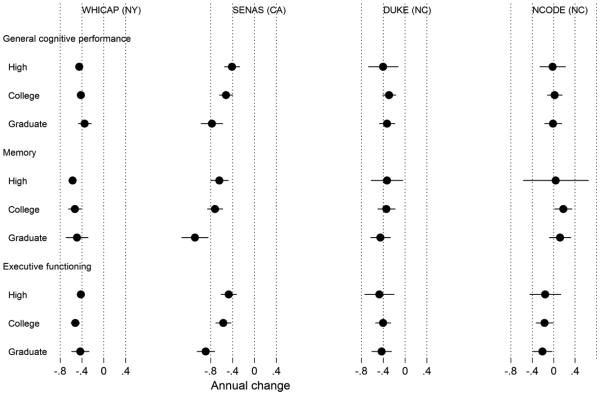
Figure 6. Model-estimated annual change in general cognitive performance, memory, and executive function by study and education level (N=5,803).
Legend. This plot shows estimated annual rates of change for each education and study group. Results from a parallel process latent growth curve model of general cognitive performance, memory, and executive function in the pooled sample, with indicators for level of education, study, and control variables (sex, clinical diagnostic status, depressive symptoms in Neurocognitive Outcomes of Depression in the Elderly [NCODE]). Age from 75 years was the timescale of interest. The x-axis is on a T-score metric (mean 50, standard deviation 10) scaled to a national metric using the Aging, Demographics, and Memory Substudy Health and Retirement Study (ADAMS HRS) study. The model-estimated variance for annual changes in general cognitive performance, memory, and executive function was 0.025, 0.064, and 0.009, respectively.
WHICAP = Washington Heights-Inwood Columbia Aging Project; SENAS = Spanish and English Neuropsychological Assessment Scales; Duke MHA = Duke Mental Health and Aging Study; NCODE = Neurocognitive Outcomes of Depression in the Elderly.