Fig. 7.
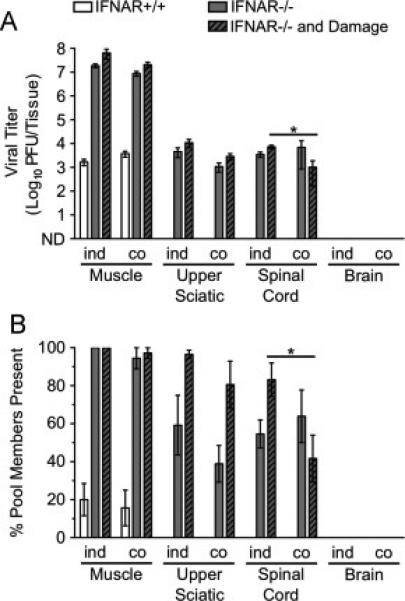
Co-infection with poliovirus does not enhance reovirus dissemination to the CNS. IFNAR+/+ and IFNAR−/− mice were inoculated intramuscularly with 107 PFU total of nine genetically marked reoviruses and 107 PFU total of 10 genetically marked polioviruses. Tissues were collected at 72 hpi. Reovirus titers and population diversity were determined by plaque assay and hybridization-based assay, respectively, using L929 cells, which do not support poliovirus replication. Reovirus T3D titer (A) and viral population diversity (B) in tissues harvested from adult IFNAR+/+ or IFNAR−/− mice with or without muscle damage. ‘ind’ indicates data from infections with reovirus only (from Fig. 6A-B data), and ‘co’ indicates data from the reovirus-poliovirus co-infection. Results are presented as mean +/− standard error of the mean from 5-7 mice per condition. Values that are significantly different, as determined by the Mann-Whitney test, are indicated by asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05. ND, none detected.
