Figure 1.
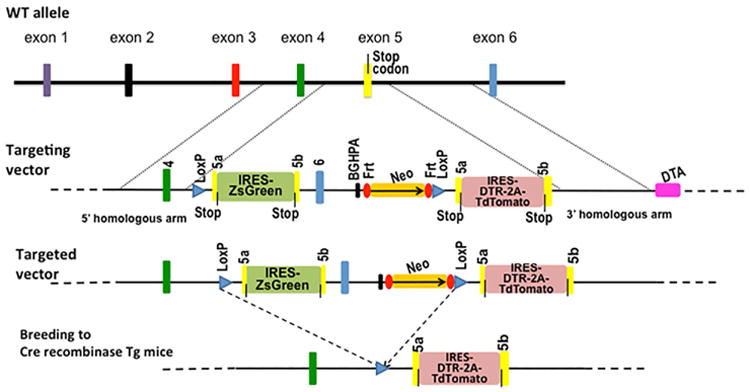
Genetic targeting strategy. A cDNA copy of ZsGreen, a green fluorescent protein, was inserted after the stop codon in exon 5 (yellow bar) of the PD-L2 gene, separated by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). A neomycin-resistance gene (Neo) and a BGHPA sequence were inserted after exon 6 (blue bar). All these insertions were flanked by two LoxP sequences (blue triangles). A duplication of exon 5 was inserted after the 3′-end LoxP sequence. An IRES and a cDNA copy of diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) were inserted after the stop codon in the duplicate exon 5 followed by a cDNA copy of the red fluorescent protein TdTomato. The DTR and TdTomato genes were separated by a DNA sequence coding a 2A self-cleavage peptide. After crossing to a Cre recombinase transgenic mouse, the sequence flanked by LoxP sites will be removed permanently, leaving only the IRES–DTR–2A–TdTomato sequence.
