FIG 4.
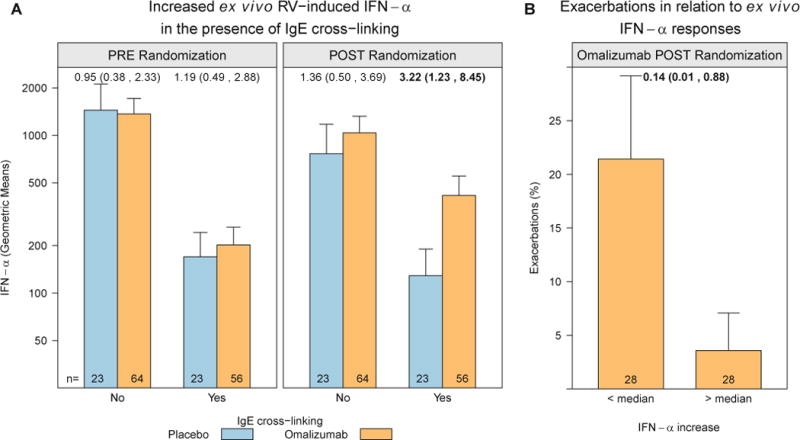
Enhanced ex vivo IFN-α responses to rhinovirus (RV) in the omalizumab group and relationship to exacerbation rates. PBMCs were incubated ex vivo with rhinovirus in the presence or absence of an IgE cross-linking antibody, and IFN-α levels were measured in culture supernatants. Rhinovirus-induced IFN-α was significantly reduced by IgE cross-linking; the IFN-α response was significantly increased in the omalizumab group during the intervention phase of the study. A, A 3.22-fold increase in omalizumab versus placebo in the postrandomization phase (P = .03). B, Among participants treated with omalizumab, those with the greatest increase in ex vivo IFN-α responses in the presence of IgE cross-linking were less likely to have an asthma exacerbation during the outcome period. Values at the top of each panel are ORs (95% CIs).
