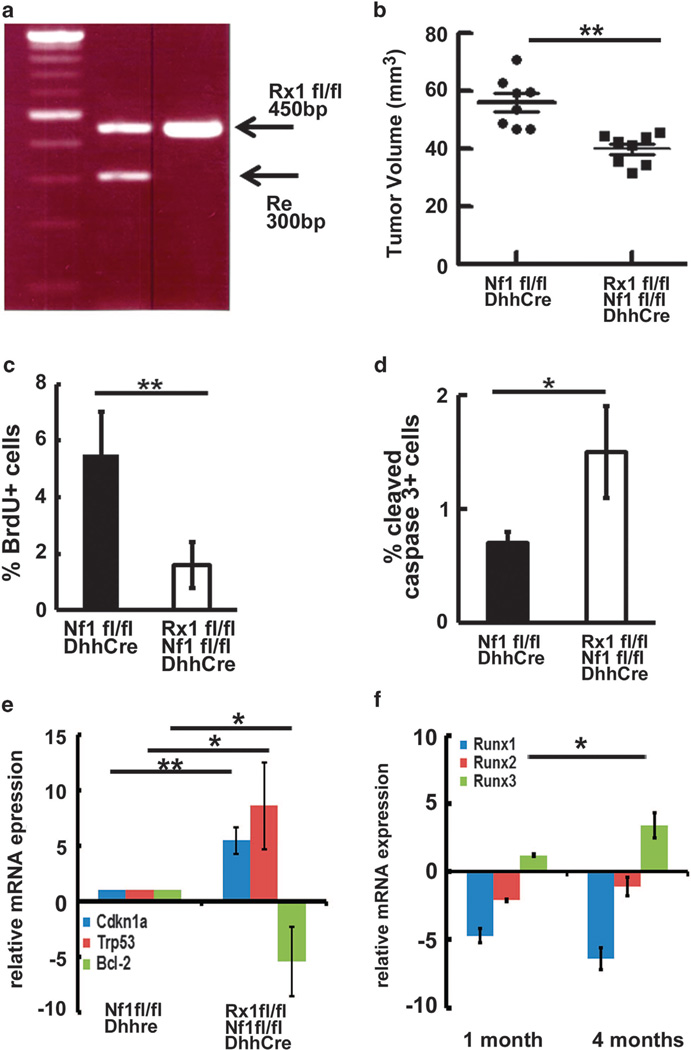
Figure 3.
Targeted genetic deletion of Runx1 in SCs and SCPs delays mouse neurofibroma formation in vivo. (a) The animal care and use committees of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center approved all animal procedures. Mice were housed in temperature- and humidity-controlled facilities on 12-h dark–light cycles with free access to food and water. We bred the Runx1fl/flmice onto the Nf1fl/fl background to obtain F1 generation (Runx1fl/+;Nf1fl/+). We also bred the Runx1fl/fl mice with Nf1fl/+;DhhCre+ to obtain Runx1fl/+;Nf1fl/+;DhhCre mice. We then bred Runx1fl/+;Nf1fl/+with Runx1fl/+;Nf1fl/+;DhhCre mice to obtain Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre mice. Littermates, Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre mice or Runx1fl/+;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre, served as controls. PCR genotyping of Runx1fl/fl mouse. (b) Volumetric measurements on 4-month-old Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl; DhhCre (n = 8) and Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre mice (n =8). (c) BrdU analysis on Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (black) and Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (white). (d) Cleaved caspase 3 analysis on Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (black) and Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (white). (e) qRT–PCR of the indicated genes. mRNAs were extracted from the DRG/tumors of Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (n =3) or Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (n =3) mice at 4 months of age. qRT–PCRs were performed as above. (f) qRT–PCR of Runx1, Runx2 and Runx3 from DRG/tumors of Runx1fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre (n =3) mice at 1 month and 4 months of age and age-matched wild-type mouse sciatic nerves. Relative mRNA expression levels were normalized to wild-type mouse sciatic nerves gene expressions. **P <0.01, *P <0.05.