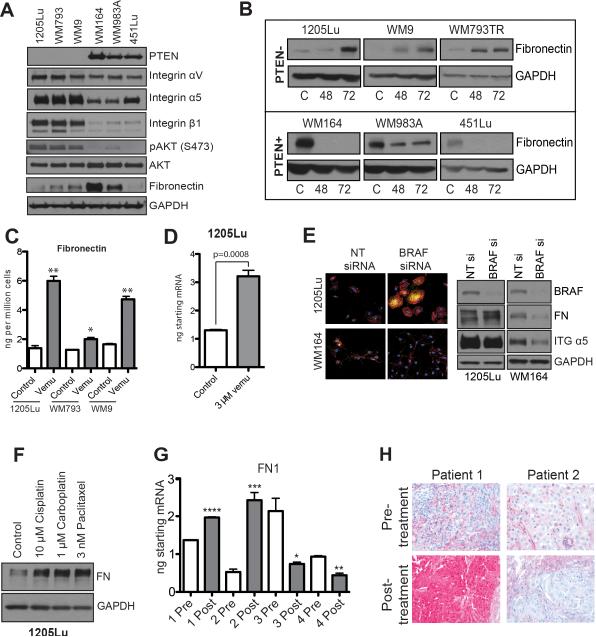
Figure 2. Vemurafenib induces FN expression.
A: Western blot showing expression of PTEN, integrin αV, integrin α5, integrin β1, FN pAKT (Ser473) and AKT in three BRAF6000E/PTEN+ melanoma cell lines (WM164, WM983A, 451Lu) and three that are BRAF6000E/PTEN- (1205Lu, WM793, WM9). B: Vemurafenib induces FN expression in BRAF6000E/PTEN- melanoma cell lines. Western blot showing the induction of FN expression following 48- and 72-hour 3μM vemurafenib treatment. C: ELISA showing vemurafenib-mediated induction of fibronectin secretion from 3 BRAF6000E/PTEN+ cell lines. D: qRT-PCR showing vemurafenib-mediated induction of fibronectin mRNA expression in the 1205Lu melanoma cell line. E: siRNA knockdown of BRAF induces FN expression (yellow) in 1205Lu cells (PTEN-) and reduces expression in WM164 cells (PTEN+), phalloidin staining for the cytoskeleton is shown in red. F: Cytotoxic chemotherapy induces FN expression in 1205Lu PTEN- melanoma cells. Cells were treated with 10μM cisplatin, 1μM carboplatin and 3nM paclitaxel for 72 hours before being analyzed by Western blot (right). G: Some melanoma patients failing BRAF inhibitor therapy show increased intratumoral FN mRNA expression. Data shows q-RT-PCR experiments on 4 matched (pre and post treatment) pairs of melanoma patient specimens receiving vemurafenib therapy (960 mg BID), statistics calculated based on technical replicates. H: Increased FN staining in a melanoma specimen from a patient with a tumor resistant to vemurafenib therapy. Data show IHC staining for FN pre- and post-vemurafenib treatment (N=3, 960 mg BID).