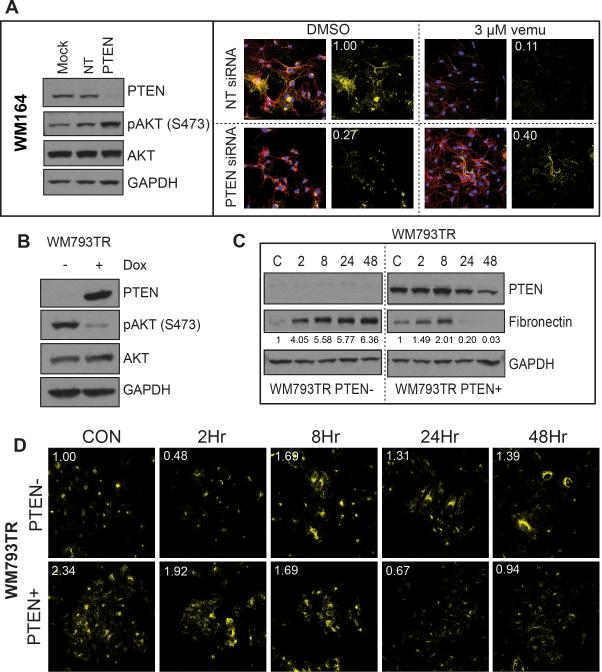
Figure 3. Treatment-associated induction of fibronectin is PTEN-dependent.
A: Knockdown of PTEN leads to FN induction following BRAF inhibition. (left) siRNA knockdown of PTEN in WM164 cells (PTEN+) leads to increased AKT signaling. (right) Immunofluorescence studies showing increased FN staining (yellow) following vemurafenib treatment in cells with PTEN siRNA knockdown (3 μM, 48 hrs.), phalloidin staining for the cytoskeleton is shown in red. B: Doxycyclinemediated induction of PTEN in the WM793 (PTEN-) cell line. Western blot shows the induction of PTEN to reduce AKT phosphorylation (48 hours). C: Induction of PTEN reduces FN expression following vemurafenib treatment. Following either induction or non-induction of PTEN WM793-TR cells were treated with vehicle or vemurafenib (3 μM, 2-48 hrs.) and FN expression was measured by Western blot. D: Immunofluorescence staining showing loss of vemurafenib-associated FN upregulation (yellow) after PTEN induction.