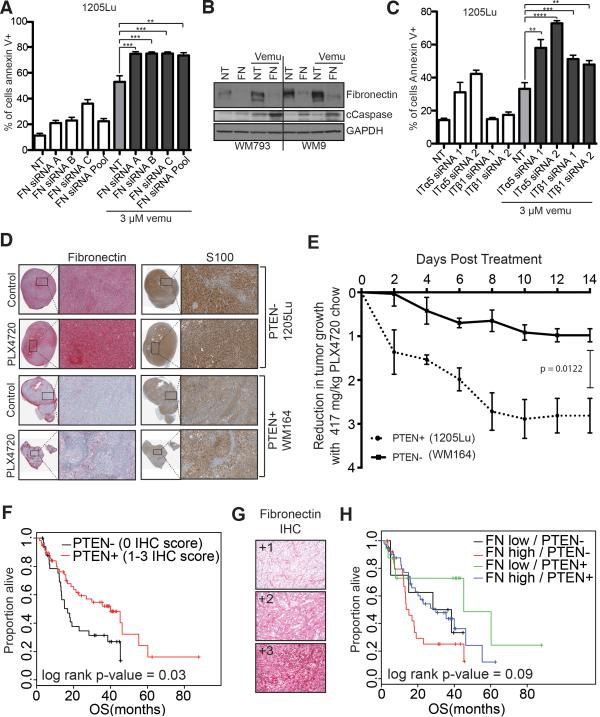
Figure 4. Integrin/FN signaling is required for melanoma cell survival on therapy.
A: siRNA knockdown of FN enhances vemurafenib mediated cell death. 1205Lu melanoma cells were transfected with three individual siRNAs and an siRNA pool targeting FN followed by treatment with vemurafenib (3 μM, 72 hours). Annexin V staining was measured by flow cytometry. B: Knockdown of FN enhances vemurafenib-mediated caspase cleavage. WM793 and WM9 cells were treated with either non-targeting or FN siRNA prior to treatment with vemurafenib (3 μM, 24 hours). Western blot shows levels of FN, cleaved caspase-7 (cCaspase) and GAPDH C: Knockdown of α5 and β1 integrin enhance vemurafenib-induced (3 μM, 48 hrs.) apoptosis in 1205Lu cells. Annexin V staining was measured by flow cytometry. D: Vemurafenib induces fibronectin expression, leading to reduced anti-proliferative effects in the 1205Lu BRAF6000E/PTEN- human melanoma xenografts, compared to the WM164 BRAF6000E/PTEN+ xenografts. IHC of representative xenograft tumors show staining for FN (red) and S100 (brown). E: Tumor volume was measured using calipers, and tumor reduction was compared by calculating the fold-decrease in tumor volume (tumor v olume = 1/2 x L x W 2). F: Lack of PTEN and high fibronectin expression predicts for worse overall survival in melanoma patients. Overall survival curve for a cohort of melanoma patients (n=93). G: Representative FN IHC staining on the tissue microarray. H: Lack of PTEN expression and high FN expression predicts for worse overall survival in melanoma patients. Overall survival curve for a cohort of melanoma patients (n=92).