Figure 5.
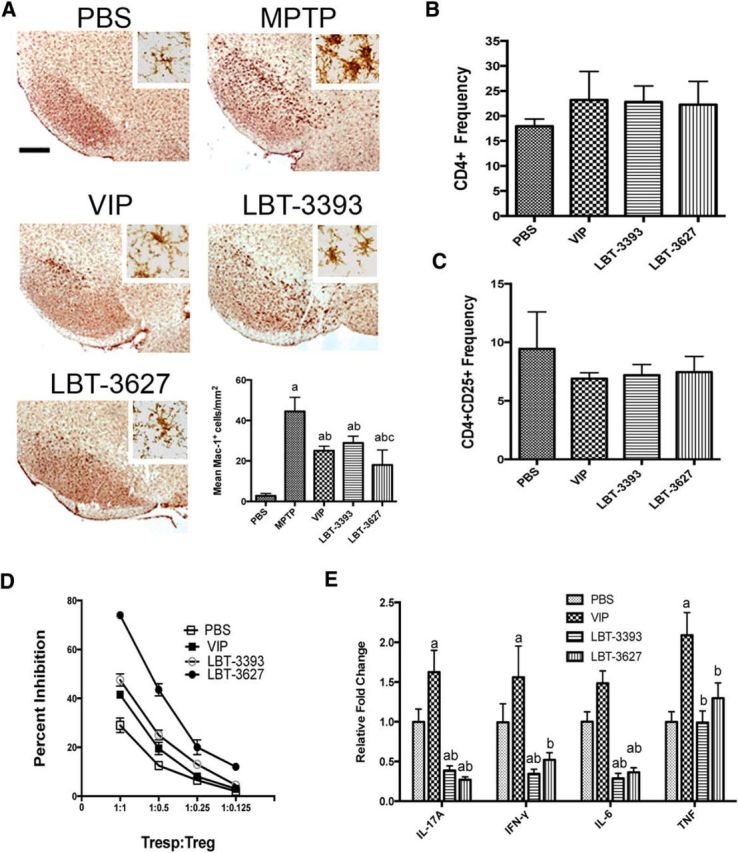
Pretreatment with VIPR agonists elicits changes in microglial reactivity and T-cell phenotypes during MPTP-induced inflammation. A, Photomicrographs of Mac-1+ microglia in the SN of PBS- or MPTP-treated mice pretreated with VIP, LBT-3393, or LBT-3627 (40× image; scale bar, 200 μm; inset = 200× image). Bottom right, Quantification of reactive microglia taken from midbrains 2 d after MPTP treatment, visualized as described in Figure 4. B, C, Mice were treated with PBS, VIP, LBT-3393, or LBT-3627 for 5 d and splenocytes assessed for frequencies of CD4+ T cells (B) and CD4+CD25+ Tregs (C). D, Assessment of Treg-mediated inhibition (±SEM) of CFSE-stained CD4+ Tresps that were stimulated for proliferation with anti-CD3/CD28. Tregs were isolated from PBS-, VIP-, LBT-3393-, or LBT-3627-treated mice. E, Relative concentration of proinflammatory cytokines in cell culture supernatants of anti-CD3-/CD28-stimulated CD4+ T cells after pretreatment (±SEM, n = 3). Cytokine concentrations were determined by cytokine bead array for pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. A, Differences in means (± SEM, n = 6) were determined where p < 0.05 compared with groups treated with PBS (a), MPTP (b), or LBT-3393 (c). E, Differences in means (±SEM, n = 3) were determined where p < 0.05 compared with groups treated with PBS (a) or VIP (b).
