Figure 1.
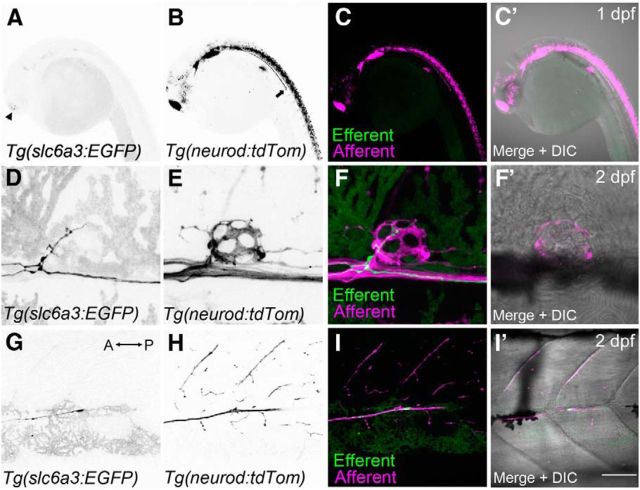
Innervation of lateral-line hair cells by dopaminergic fibers during early development. Efferent and afferent fibers were visualized in developing embryos by crossing two transgenic lines: Tg(slc6a3:EGFP) and Tg(neurod:tdTomato). A, Faint GFP expression is detected within the head at 1 dpf (arrowhead). B, tdTomato-positive fibers representing cranial and lateral-line afferent neurons at 1 dpf. Arrow indicates the lateral-line nerve extending down the trunk. C, Overlays of A (green) and B (magenta). C′, Overlay that includes the corresponding DIC image. D, Presence of a GFP-positive efferent fiber innervating the first trunk neuromast (L1) near the swim bladder at 2 dpf. E, Corresponding afferent fibers for the neuromast in D. F, F′, Overlays of D and E, respectively. G, Example of an efferent growth cone trailing after the afferent fibers (anterior posterior axis indicated by arrow). H, Corresponding afferent fibers for the same image shown in G (2 dpf). I, I′, Overlays of G and H, respectively. Scale bar: A–C′, 20 μm; D–F′, 5 μm; G–I′, 30 μm.