Figure 5.
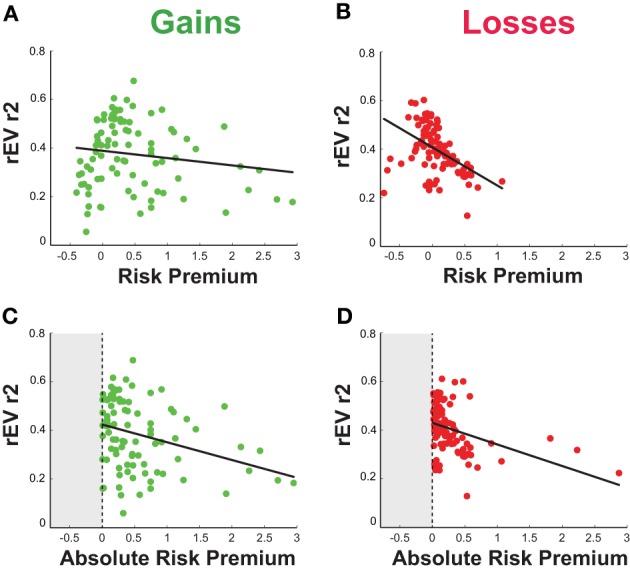
Relationship between individual risk premium and the degree to which participants relied upon the relative expected value (rEV) information in their choices in the (A) gains and (B) losses domains. A significant negative correlation is present for losses. Relationship between individual deviation from neutral risk preference (absolute risk premium accounting for the non-linearity across zero) and reliance upon the rEV information in the (C) gains and (D) losses domains. The vertical dashed line is drawn at risk neutrality (premium = 0), and the now-unattainable negative region is shaded gray. Following this transform, significant negative correlations are seen in both domains, indicating that as participants relied more heavily on the rEV information, their risk preferences became more risk neutral.
