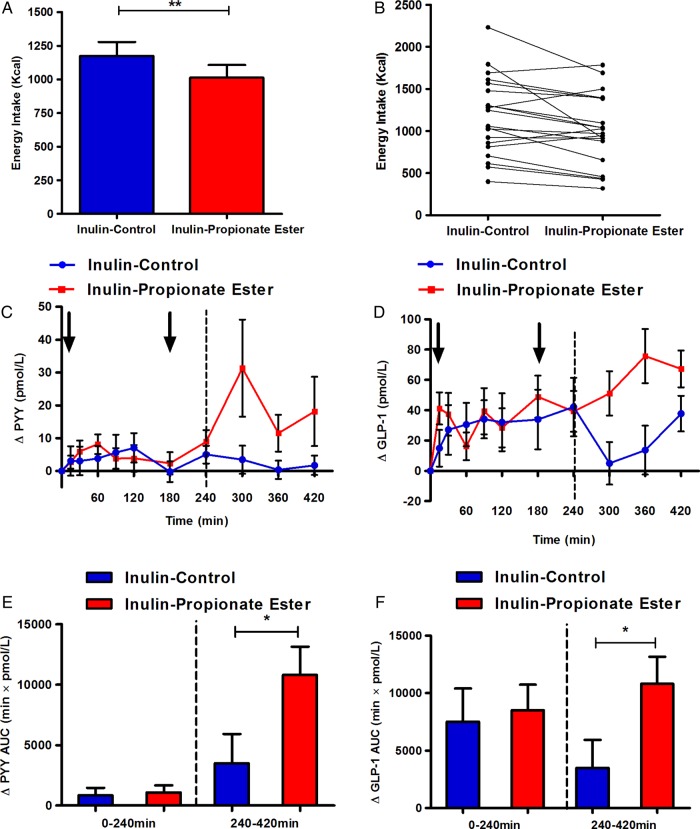
Figure 2.
Acute inulin-propionate ester supplementation increases plasma peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels and reduces energy intake in humans. (A) The mean reduction in energy intake following inulin-control versus inulin-propionate ester. (B) A reduction in energy intake occurred in 16 of the 20 volunteers. (C–F) Plasma gut hormone levels following acute supplementation of inulin-control versus inulin-propionate ester. Arrows indicate standardised meals. Dotted lines signify the time point after which >80% inulin-propionate ester enters the colon as determined by the enrichment of 13C in expired air and breath H2 methodology (figure 1C). Data are presented as mean±SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. AUC, area under the curve.