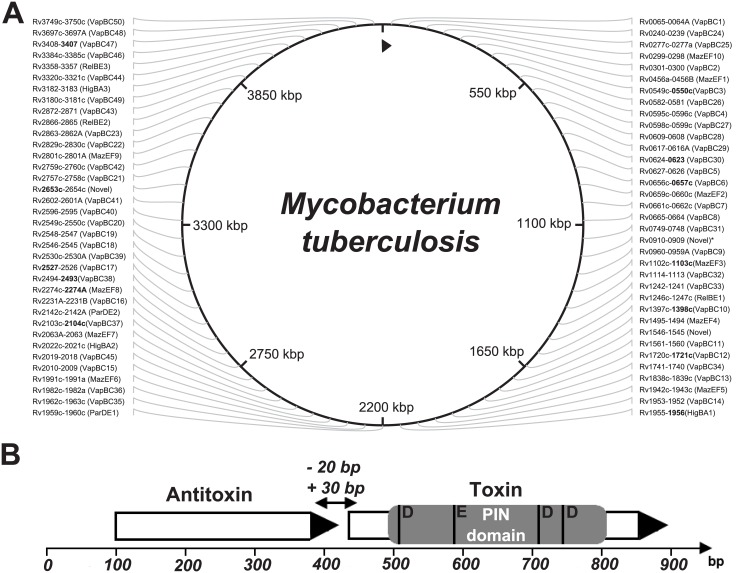
Fig 1. The type II TA systems of mycobacteria were investigated. Schematic diagram of the toxin-antitoxin system.
(A) TA systems are annotated according to the GenBank database, excluding VapBC50 (rv3750c-rv3749c), VapBC49 (rv3180c-rv3181c), HigBA3 (rv3182-rv3183), HigBA2 (rv2022c-rv2021c), MazEF10 (rv0298-rv0299) and VapBC45 (rv2018-rv2019) systems; these systems are annotated according to Sala et al. [32]. The system RelBE3 (rv3358-rv3357, GenBank database, NCBI) is called the YefM/YoeB system by Sala. All of the TA systems depicted here are type II (systems marked with an asterisk are novel TA systems that are not classified to any family, but for which functional activity has been shown [32]). The 13 genes, our proposed set for genotyping, are highlighted in bold. (B) Type II TA systems are encoded by two genes, a toxin and an antitoxin, that form one operon with a promoter located upstream of the first antitoxin gene. PIN domain is the functional part of the toxin gene, the four conserved acidic residues marked at the picture: the three well-conserved acidic residues, at positions 4[D], 40[E] and 93[D], and with fourth acidic residue is less well conserved at position 112[D].