Figure 3.
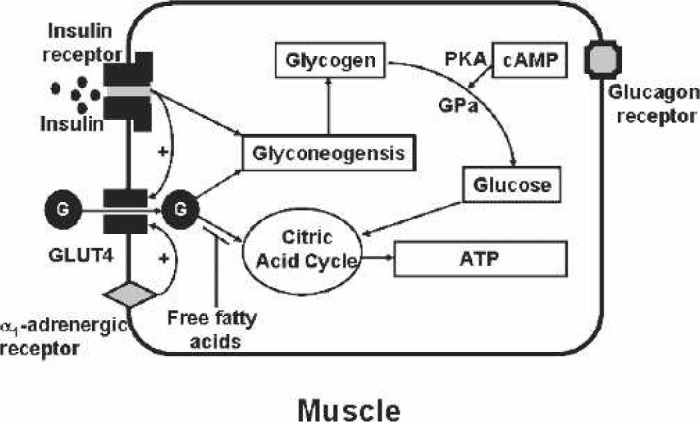
Muscle. Glucose (G) is transported into muscle by the insulin-sensitive glucose transporter, GLUT4. Either insulin receptor or α1-receptor stimulation can cause the translocation of the GLUT4 from the cytosol to the membrane. The glucose can be converted into ATP by the citric acid cycle or to glycogen. Increased free fatty acids inhibit the glucose conversion to ATP. Glucagon receptor stimulation induces cyclic-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and thereby protein kinase A (PKA). PKA activates glycogen phosphorylase (GPa) that produces glucose from glycogen.
