Figure 4. Universal vector for mono-promoter-driven CRISPR/Cas9 system.
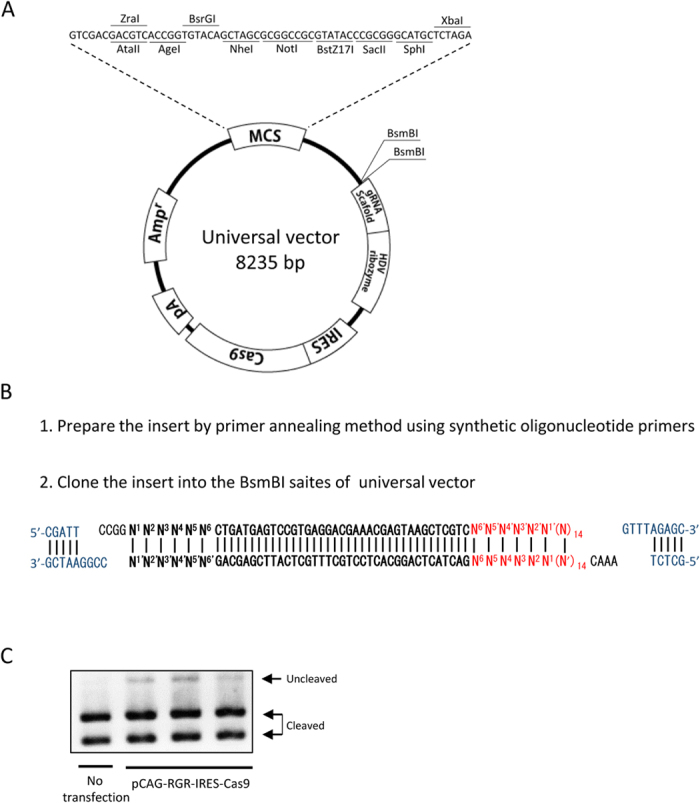
(A) Schematic illustration of the universal vector. (B) Sequence of RGR insertion. The portion of the RGR sequence containing additional nucleobases, which is necessary for the ligation, is prepared by the annealing of single strand oligonucleotides, followed by insertion into the BsmBI-digestion site of the plasmid vector. Blue characters indicate the sequence of the universal vector, red characters indicate the target sequence and bold characters indicate the HH ribozyme sequence. The first 6 bases of the HH ribozyme, from N1 to N6, must be matched with the 5′-end of the gRNA (underlined) for the function of HH ribozyme. (C) Restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis. HEK 293 cells (1 × 105) were transfected with HPRT1 targeting pCAG-RGR-IRES-Cas9 vector (1 μg) reconstructed from the universal vector, and the genomic DNA of the cells was extracted 72 h after transfection. The DNA was subjected to PCR, and 300 ng of the PCR products was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis after incubation with XcmI. Experiments were conducted using 3 plasmid clones of the same vector, and the results were similar to those of non-transfected cells. Cleaved and uncleaved fragments indicate unmodified and modified genomes, respectively.
