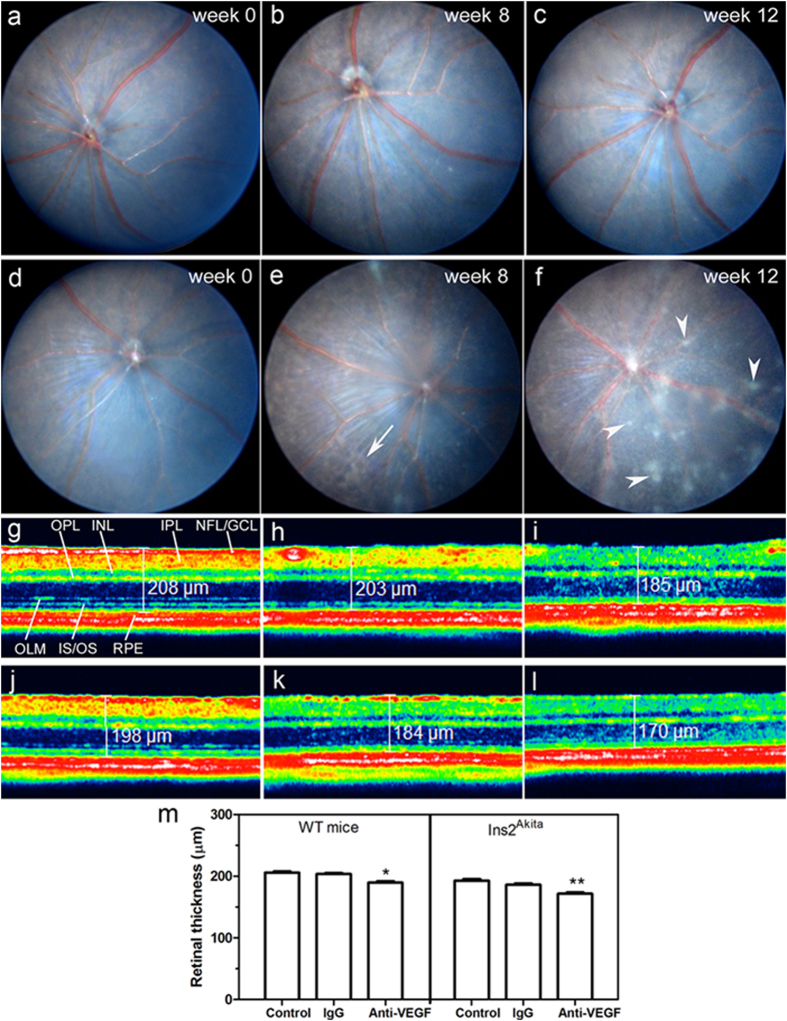
Figure 1. Clinical examinations following intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF.
Fundus images from WT (a–c) or Ins2Akita (d–f) mice at baseline (week 0) (a,d), 8 weeks (b,e) or 12 weeks (c,f) after intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF. Arrows indicate brownish irregular shaped lesions; Arrowheads indicate cotton wool spot-like lesions. SD-OCT representative images from WT (g–i) or Ins2Akita (j–l) mouse retinas of non-injected controls (g,j), intravitreal IgG (h,k) or anti-VEGF (i,l) treated mice at 12 weeks post-injection. (m) Quantitative analysis of neuroretinal thickness in WT and Ins2Akita non-injected, IgG or anti-VEGF treated mice (n = 6 eyes per strain/condition). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to non-injected controls of the same strain. One-way ANOVA. NFL/GCL, nerve fibre/ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; OLM, outer limiting membrane; IS/OS, photoreceptor inner/outer segments; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.