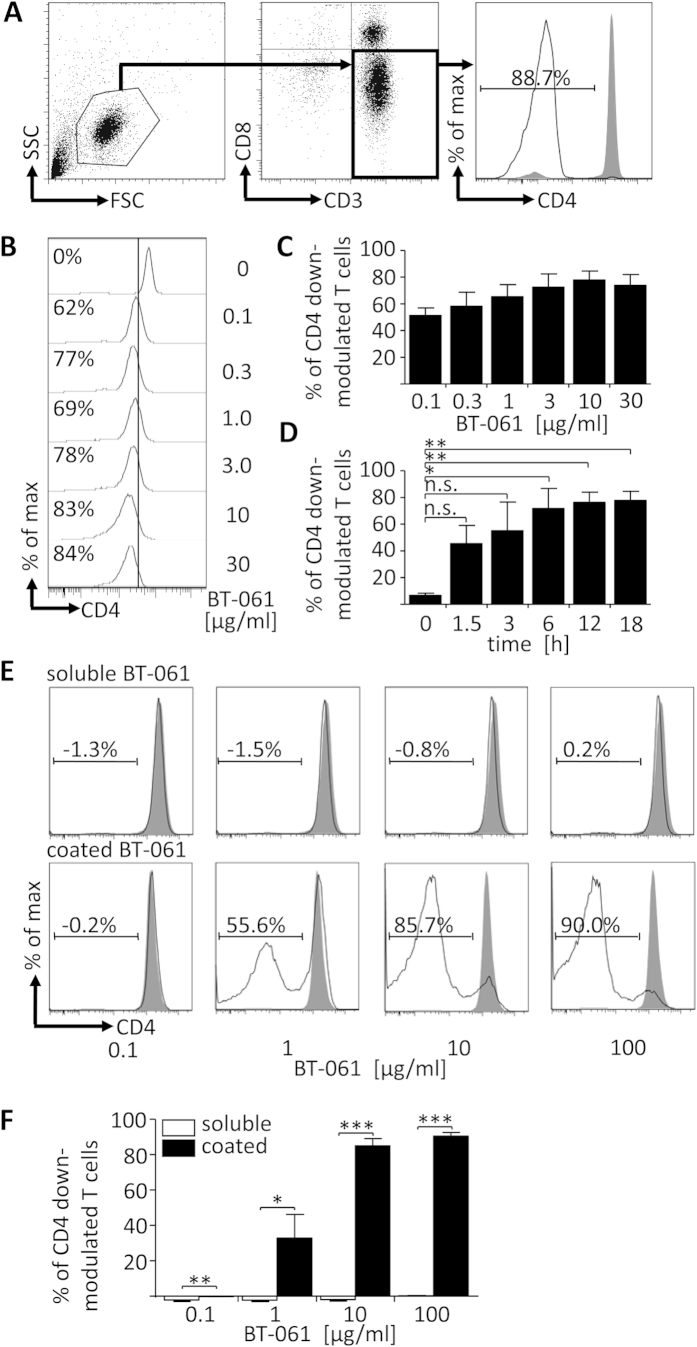
Figure 1. BT-061 treatment of PBMC induces CD4 down-modulation of T cells.
(A) CD3+ T cells were stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD8a, and anti-CD4 clone SK3 that binds a different epitope than BT-061 (filled grey), or an isotype control (black line). In cytometric analysis CD3+CD8- T cells were defined as CD4 down-modulated and their percentage was calculated. (B) PBMC were treated with the indicated concentrations of BT-061 for 45 min at 4 °C and then cultivated for 18 h at 37 °C. CD4 expression of T cells was determined cytofluometrically. One experiment of 2 similar ones with cells derived from 3–5 donors is shown. (C) Statistical analysis from all experiments as shown in (B). (D) PBMC were treated with BT-061 (10 μg/ml) for 45 min at 4 °C and then cultivated for the indicated times at 37 °C. CD4 expression was determined cytofluometrically. Statistical analysis of 2 similar experiments with cells derived from 3–5 donors. (E) Purified CD3+ T cells were treated with BT-061 (as in B, black line) or with medium (filled grey) and then incubated for 18 h at 37 °C (upper row). Purified CD3+ T cells were cultured for 18 h at 37 °C in wells coated with BT-061 at the indicated concentrations (black line) or in untreated wells (filled grey) (lower row). CD4 expression was determined cytofluometrically. Representative data of one experiment from cells derived from 3 donors (upper row) or from 2 similar experiments with cells derived from 5 donors (lower row) are shown. (F) Statistical analysis from all experiments as shown in (E). Error bars indicate SEM.