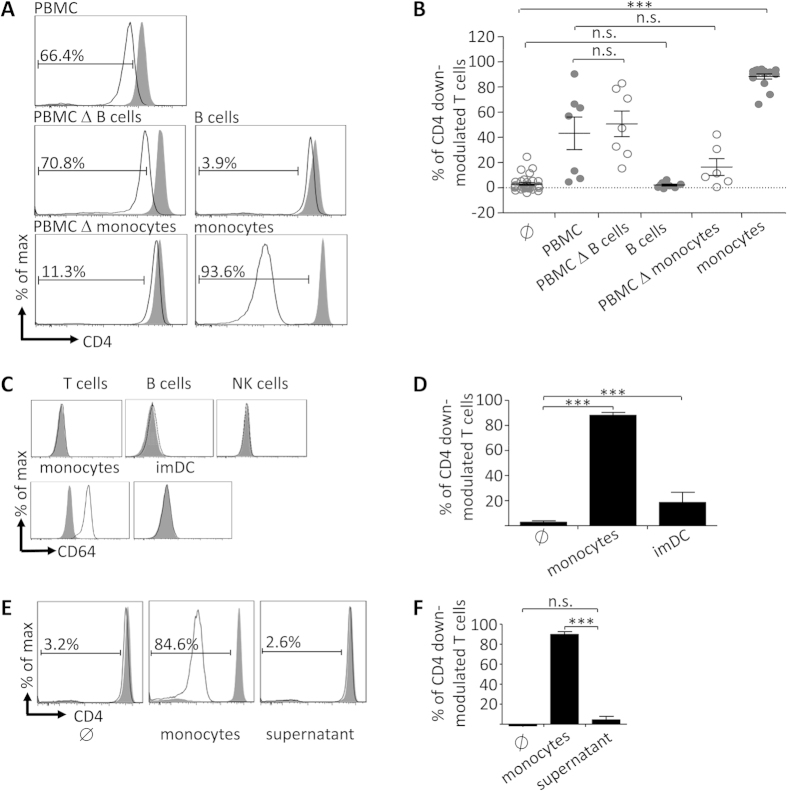
Figure 2. Monocytes confer robust CD4 down-modulation of BT-061-decorated T cells by cell-cell-contact.
(A) BT-061 decorated (black line) or medium treated (filled grey) CD3+ T cells were cultivated for 18 h at 37 °C either in medium (∅), with PBMC, with immune cell subsets (as indicated), or with PBMC depleted of the respective immune cell subsets. Representative data are shown of 4 experiments performed with cells from 7 donors (PMBC), 4–5 experiments with cells from 7–8 donors (B cell depleted PBMC or B cells), and 4–8 experiments with cells from 6–15 donors (monocytes depleted PBMC or monocytes). (B) Statistical analysis from the experiments in (A). (C) CD3+ T cells, CD19+ B cells, CD56+ NK cells, CD14+ monocytes and HLA-DR+ CD14– immature moDC (imDC) were stained for CD64 (black lines) or isotype control (filled grey). Representative data from 3 experiments are shown. (D) BT-061 decorated T cells were co-cultured with monocytes or imDC for 18 h at 37 °C. Statistical analysis of 4–8 experiments with cells from 6–15 (monocytes) and one experiment with cells from 4 donors (imDC). Error bars indicate SEM. (E) BT-061 decorated (black line) or medium treated (filled grey) CD3+ T cells were cultivated for 18 h at 37 °C together with monocytes (middle panel), or incubated in cell-free supernatant taken from BT-061 decorated T cells co-incubated with monocytes for 18 h (right panel). Data are shown of two experiments with cells from 3 donors. (F) Statistical analysis from all experiments as shown in (E).