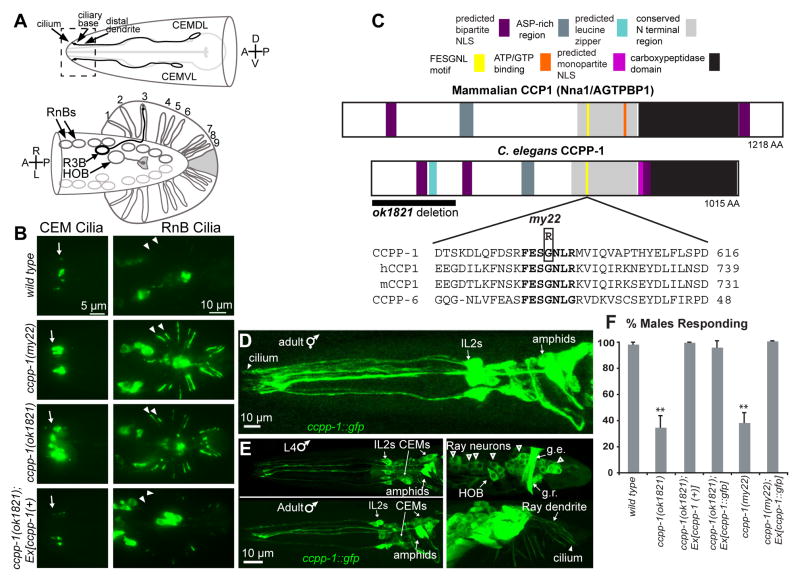
Fig. 1. CCPP-1 is required for PKD-2 localization and is expressed in the ciliated sensory nervous system.
A Diagram of the male-specific CEM neurons in the head, and HOB and RnB neurons in the tail. Box illustrates the region of CEM cilia and distal dendrites shown in the epifluorescent images. In the ventral-up cartoon of the male tail, the RnBs innervate the tail rays; R3B dendrite is shown as an example. B In wild-type males, PKD-2::GFP faintly illuminated cilia of the CEM neurons, the HOB cilium, and the cilia of the ray B-type neurons (RnB, where n = 1 – 9, excluding 6). ccpp-1(my22) and ccpp-1(ok1821) mutants exhibit the Cil phenotype. Arrows point to CEM cilia; arrowheads point to R1B and R2B cilia. Expression of genomic ccpp-1 rescued the Cil phenotype of ccpp-1(ok1821). C CCPP-1 contains several conserved regions, including a zinc carboxypeptidase domain, an aspartic-acid rich domain, a conserved “NT” region [12], and predicted NLS (nuclear localization signal; [35]). CCPP-1 also contains a predicted leucine zipper near the N-terminus (ScanProsite, [36]). The my22 lesion affects the conserved sequence FESGNL in the NT region of CCPP-1. D In adult hermaphrodites, CCPP-1::GFP expression was expressed in amphid and IL2 core ciliated sensory neurons. Cilium containing CCPP-1::GFP is indicated. E Confocal projections of CCPP-1::GFP expression in males. Top (L4): CCPP-1::GFP was expressed in (left) amphid, IL2, and CEM neurons and (right) male tail ray and HOB neuronal cell bodies (empty arrowheads). Gubernacular erector (g.e.) and retractor (g.r.) muscles are indicated. Bottom (1 day old adult): CCPP-1::GFP localization in ray neuron dendrites (arrow) and a cilium (arrowhead). F ccpp-1 mutants are defective in response behavior. Number of trials and number of males for each genotype was as follows: wild type, 7 trials, N = 70 males; ok1821, 6 trials, N = 60; ok1821;Ex[ccpp-1(+)], 3 trials, N = 29; ok1821;Ex[ccpp-1::gfp], 3 trials, N = 24; my22, 4 trials, N = 40; my22;Ex[ccpp-1::gfp], 5 trials, N = 39. Error bars indicate SEM; **indicates ccpp-1 mutants were statistically different (p < 10−4, ANOVA/Tukey HSD test) from mutants expressing ccpp-1 transgenes, which were similar to wild type. See also Fig. S1.