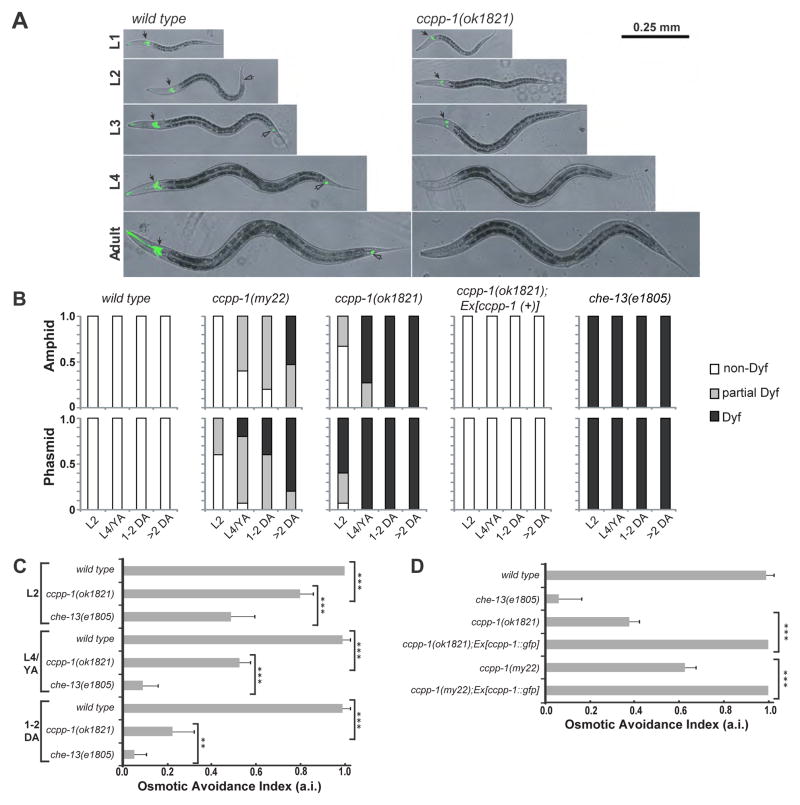
Fig. 2. ccpp-1 mutants exhibited progressive Dyf and Osm defects.
A Amphid (solid arrows) and phasmid (hollow arrows) ciliated neurons of wild type hermaphrodites were stained by DiI (pseudocolored green) at all developmental stages. ccpp-1(ok1821) amphid cilia in L1 larvae stained normally, but became Dyf in later larval stages and adults. B Dyf defects were scored in amphid and phasmid neurons in wild-type, my22, ok1821, and che-13(e1805) young adults (24 hours post-L4). 15 animals were scored for each stage/genotype. C Wild-type animals exhibit osmotic avoidance behavior when challenged with an 8 M glycerol ring. 80 hermaphrodites (8 trials, 10 per trial) were tested for each stage/genotype. Osmotic avoidance index (a.i.) is the fraction of animals that avoided crossing the ring. D The ccpp-1 Osm defect was rescued by the ccpp-1::gfp transgene (8 trials, 10 animals per trial tested). (Error bars indicate SEM; ** indicates p = 0.0022 with Fischer’s Exact Test; *** indicates p < 0.0001 with Fischer’s Exact Test).