Fig. 1. Reduced structural integrity of the corpus callosum in Fmr1−/y mice.
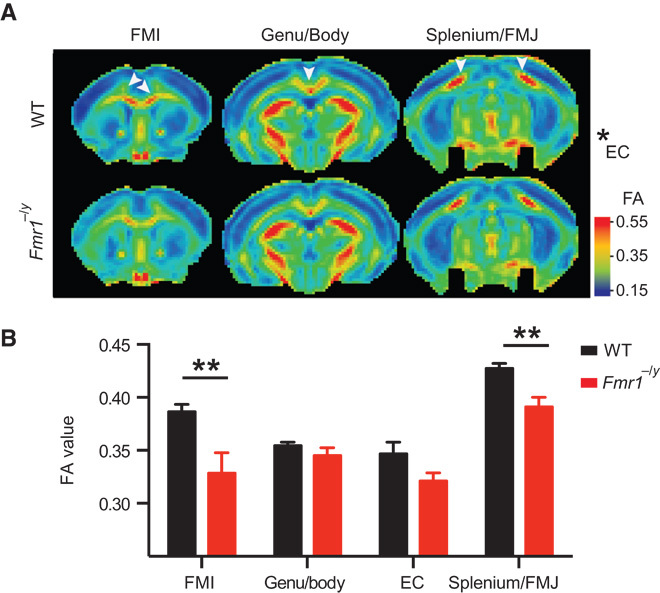
DTI was performed on adult Fmr1−/y and wild type (WT) mice to measure the FA of the corpus callosum. Tensor images were collectively acquired in several horizontal planes from +2.0 to −4.0 mm from the bregma, with an interplane distance of 0.5 mm (WT, n = 12; Fmr1−/y, n = 7). FA values were measured on individual planes and grouped into the splenium/FMJ of the corpus callosum, EC, the Genu/Body of the corpus callosum, and the FMI of the corpus callosum. (A) Color-coded heat maps of the FA values showing the average (of all WT and Fmr1−/y animals) of one plane from each group (from anterior to posterior). Warm colors indicate fiber tracts with strong diffusion coherence. (B) The FA values were significantly reduced in Fmr1−/y mice in the FMI (P = 3.5 × 10−5) and the splenium/FMJ (P = 0.0069). Data are means ± SEM. **P < 0.01 (Fmr1−/y compared with WT). Statistical significance was determined using multiple t tests corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Sidak method with α = 0.05.
