Fig. 5. Neural activity elicited by masker tones, with emphasis on the N1 latency range.
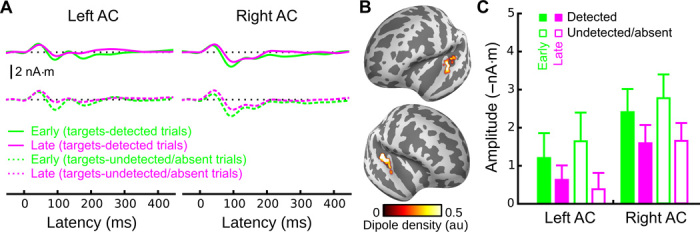
(A) Grand-average MxNE solutions. (B) Corresponding dipole locations. (C) Quantified N1 amplitudes. A three-way ANOVA with hemisphere, target detection, and time interval as factors revealed a significant main effect of interval (F1,19 = 15.1, P < 0.005) as well as a significant two-way interaction between interval and target detection (F1,19 = 5.1, P < 0.05). However, this interaction went in the opposite direction that would be expected based on an attentional account of the data (that is, the early-late difference was larger for targets-undetected and targets-absent trials; table S2). Here, the source space used for the masker-elicited N1 was the same as for the masker-elicited P1. The same pattern of results was found when the more anterior MMN-defined source space was used (cf. figs. S5 and S6).
