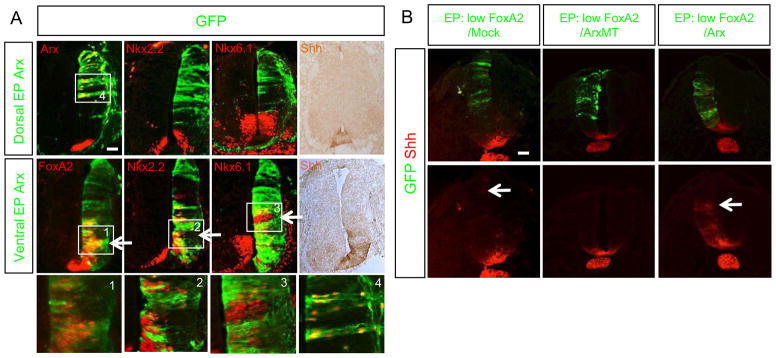
Fig. 2.
Ectopic expression of Arx induces Shh and Shh-downstream genes in the presence of FoxA2. A) In ovo electroporation (EP) of Arx to the ventral or dorsal spinal cord analyzed for Nkx2.2, Nkx6.1, FoxA2, and Shh expression via immunostaining. Arx EP to the ventral neural tube induces FoxA2, Nkx2.2, Nkx6.1 and Shh (bottom panel), while dorsally targeted Arx does not (top panel). The electroporated plasmid expresses Arx and GFP, thus the presence of GFP reports the location of ectopic Arx expression. Boxed areas labeled 1–4 corresponded to high power images at bottom of A. B) Co-electroporation of low level of FoxA2 with ArxWT (wild type) (1:10 ratio in DNA concentration) induces Shh cell non-autonomously, even in the dorsal neural tube, whereas co-electroporations of low level of FoxA2 with Arx MT (non-DNA bound homeodomain mutant; R332H) or mock DNA do not. Arrows in A and B indicate the ectopic induction of Shh or Shh downstream target genes. Scale bars in A and B are 50 μm.