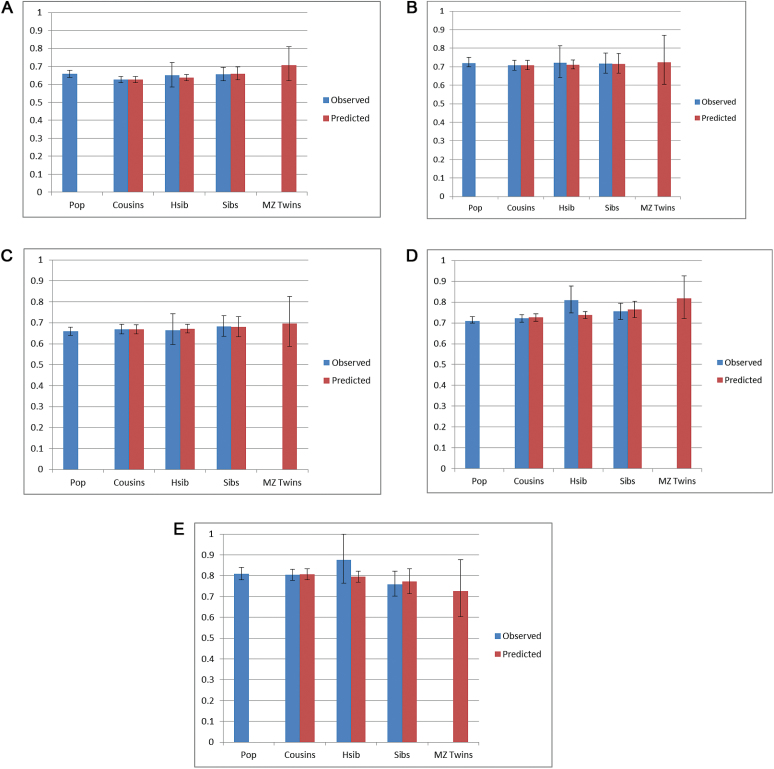
Fig. 2.
(a) Co-relative control analyses (±95% CI) for the association between school achievement and schizophrenia based on a linear HR model for males and females combined. The observed results for the general population and cousins, hsib (half siblings) and full siblings (sibs) discordant for SA are presented in blue. The associations predicted from a model fitted to the observed data in cousins, half siblings, full siblings, and monozygotic (MZ) twins are presented in red. (b). Co-relative control analyses (±95% CI) in females for the association between school achievement and other nonaffective psychoses based on a linear HR model for males and females combined. The observed results for the general population and cousins, hsib (half siblings) and full siblings (sibs) discordant for SA are presented in blue. The associations predicted from a model fitted to the observed data in cousins, half siblings, full siblings, and monozygotic (MZ) twins are presented in red. (c). Co-relative control analyses (±95% CI) in males for the association between school achievement and other nonaffective psychoses based on a linear HR model for males and females combined. The observed results for the general population and cousins, hsib (half siblings) and full siblings (sibs) discordant for SA are presented in blue. The associations predicted from a model fitted to the observed data in cousins, half siblings, full siblings, and monozygotic (MZ) twins are presented in red. (d). Co-relative control analyses (±95% CI) in females for the association between school achievement and bipolar illness based on a linear HR model for males and females combined. The observed results for the general population and cousins, hsib (half siblings) and full siblings (sibs) discordant for SA are presented in blue. The associations predicted from a model fitted to the observed data in cousins, half siblings, full siblings, and monozygotic (MZ) twins are presented in red. (e). Co-relative control analyses (±95% CI) in males for the association between school achievement and bipolar illness based on a linear HR model for males and females combined. The observed results for the general population and cousins, hsib (half-siblings) and full siblings (sibs) discordant for SA are presented in blue. The associations predicted from a model fitted to the observed data in cousins, half-siblings, full siblings, and monozygotic (MZ) twins are presented in red.