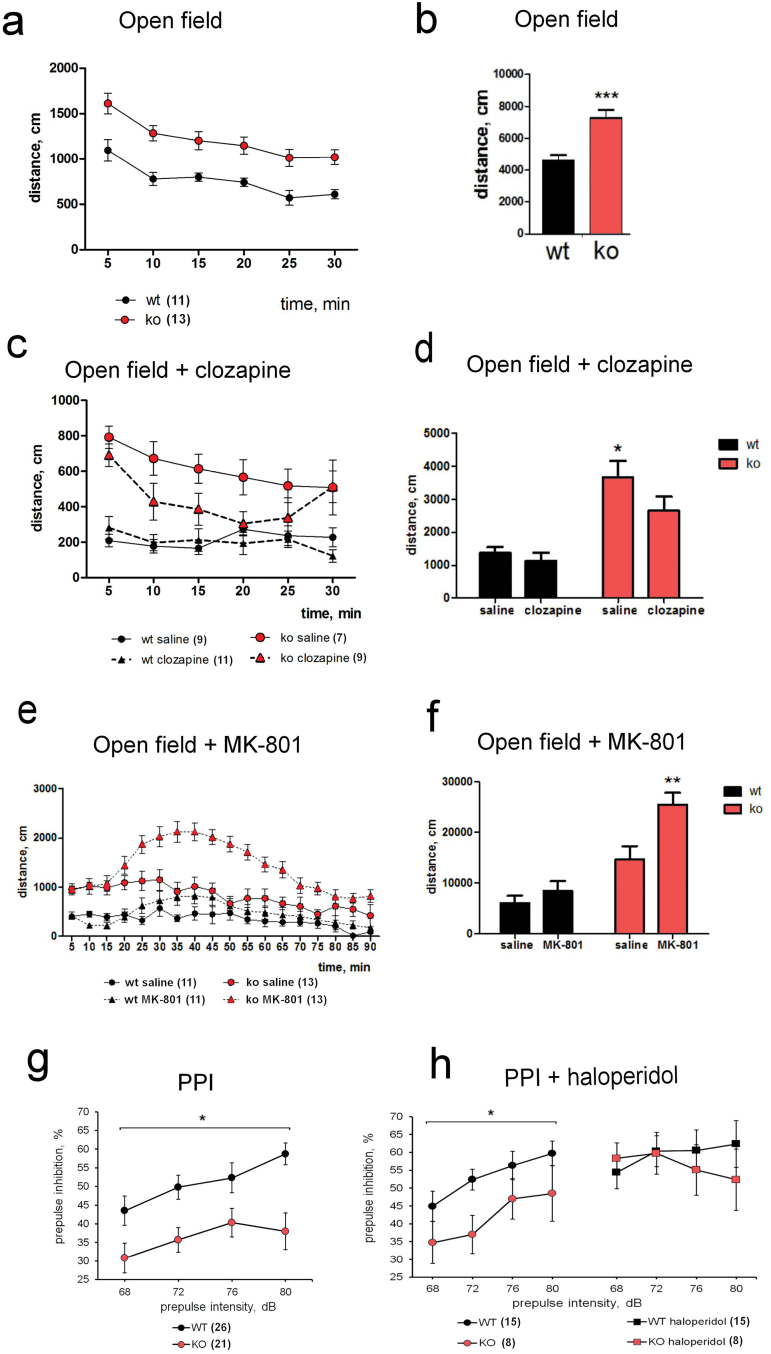
Fig. 2.
AMIGO-deficient mice display increased locomotor activity, sensitivity to psychotomimetic MK-801 and defective prepulse inhibition (PPI). (a, b) AMIGO knockout (KO) mice were hyperactive in the open field. (b)Total distance traveled during 30min was significantly higher in KO mice (158%; P = .0004). (c, d) In the open field, 1mg/kg of the antipsychotic drug clozapine reduced the locomotor activity of the KO mice, which could not be observed in the wild-type (WT) mice. (d) The total distance travelled was reduced 28% in the KO mice by the application of clozapine (P = .04, post hoc). (e, f) AMIGO KO mice were more sensitive to the locomotor activating effect of psychotomimetic MK-801 (0.2mg/kg) in the open field (f) In the WT animals, a low dose of MK-801 (0.2mg/kg) slightly increased the total distance traveled, but the effect was not significantly different from saline. In the KO animals, the same dose significantly increased the distance traveled (P = .001, post hoc). (g) The AMIGO KO mice had reduced PPI compared to the WT littermates (see table 1 for P values) (h) Antipsychotic drug haloperidol (1mg/kg) improved the impaired PPI. The number of animals used in each experiment is indicated in parentheses. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.