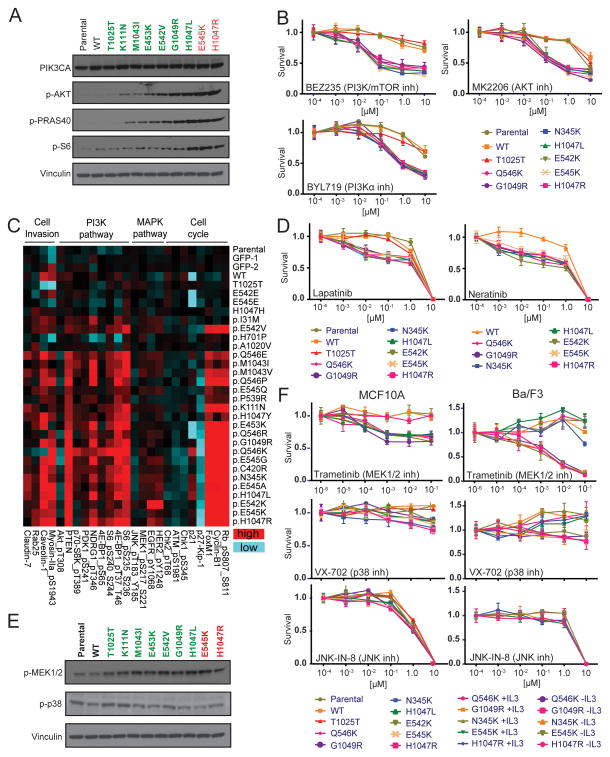
Figure 4. PIK3CA tail mutations differentially activate cancer signaling pathways and sensitize cells to pathway inhibitors.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of the indicated proteins using extracts from MCF10A cells expressing wild-type (WT), rare (green) and hotspot (red) PIK3CA variants grown in the absence of insulin and EGF. Vinculin = loading control. (B) Dose-response survival curves for the indicated MCF10A stable cell lines treated with PI3K pathway inhibitors BEZ235, MK2206 and BYL719. (C) Representative differentially expressed proteins (p<0.05) determined by RPPA, respectively, from the indicated stable MCF10A cell lines grown in the absence of insulin and EGF. Entire RPPA dataset (p<0.05) provided in Supplementary Figure S2. (D) Dose-response survival curves for the indicated MCF10A stable cell lines treated with HER2/EGFR inhibitors Lapatinib and Neratinib. (E) Immunoblot analysis of the indicated proteins using extracts from MCF10A cells expressing wild-type (WT), rare (green) and hotspot (red) PIK3CA variants grown in the absence of insulin and EGF. Vinculin = loading control. (F) Dose-response survival curves for the indicated MCF10A (left) and Ba/F3 (right) stable cell lines treated with inhibitors BEZ235, MK2206 and BYL719. For Ba/F3, the sensitivity exhibited by experimental cell lines (-IL3) is assessed by comparison with cell lines re-addicted to IL3 (+IL3) over PIK3CA variants. Error bars depict the standard deviation.