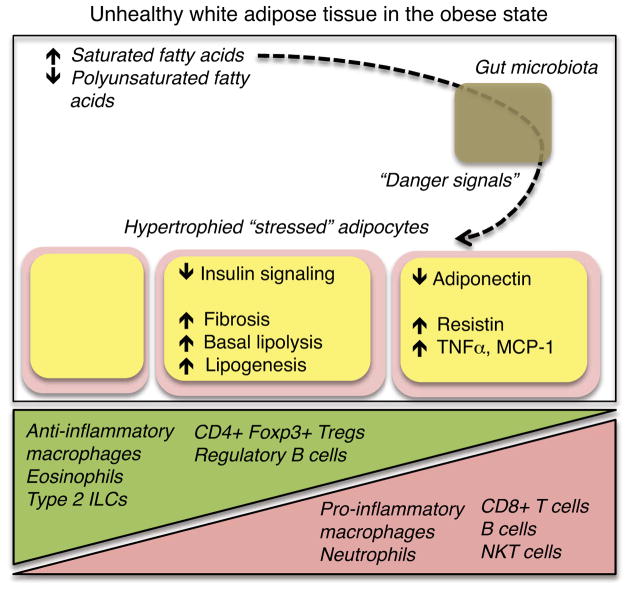
Figure 1. Inflammatory cascades that contribute to adipocyte dysfunction.
Diets high in saturated fatty acids, when consumed in a state of chronic caloric excess, contribute to adipocyte dysfunction. While healthy adipocytes are insulin-sensitive and have low levels of basal lipolysis, adipocytes that reach their lipid-storage limit and/or are exposed to chronically elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines may exhibit the dysfunctions listed above. Chronic overnutrition also disrupts the balance of immunocyte populations present in adipose tissue. A possible contributing pathway involves diet-induced alterations in gut symbionts that, through yet unclear mechanisms, triggers pathologic adipose tissue inflammation.