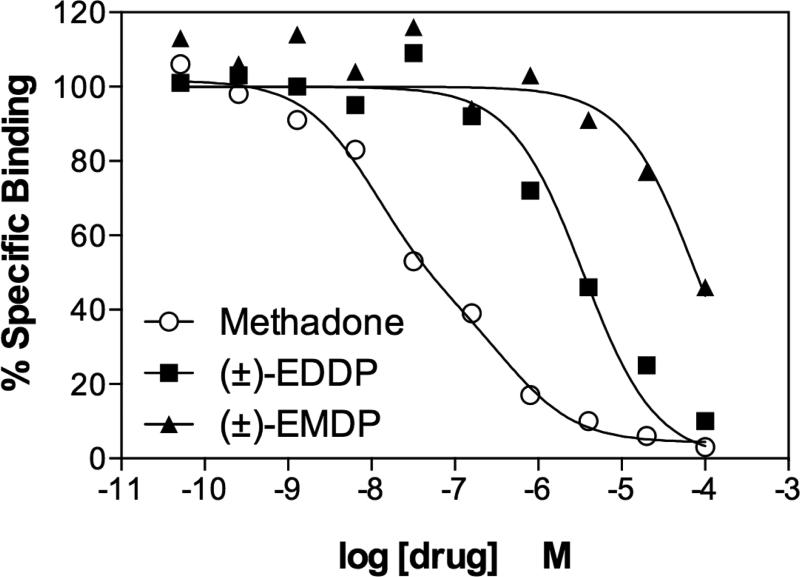
Figure 2. Methadone, EDDP and EMDP competition for opiate receptor binding sites labeled by [3H]-naloxone in rat forebrain membranes.
Opiate receptors in rat forebrain (colliculi forward) were labeled by 2 nM [3H]-naloxone (Kd is ~ 0.7 nM) in the absence or presence of (−)-methadone, (±)-EDDP or (±)-EMDP at the concentrations shown. Methadone competition curves fit a model for two sites, with the largest fraction having a high binding affinity, Ki ~ 11 nM. EDDP and EMDP competition curves fit a model for a single binding site. EDDP competed for nearly all of the binding sites but with an apparent affinity ~83-fold lower than that of methadone. EMDP competed for only 60% of the sites even at a concentration of 100 μM, and its apparent affinity was ~1900-fold lower than that of methadone. The Ki values for EDDP and EMDP were 918 nM and 21 μM, respectively. The results shown are representative of two independent assays.