Figure 7.
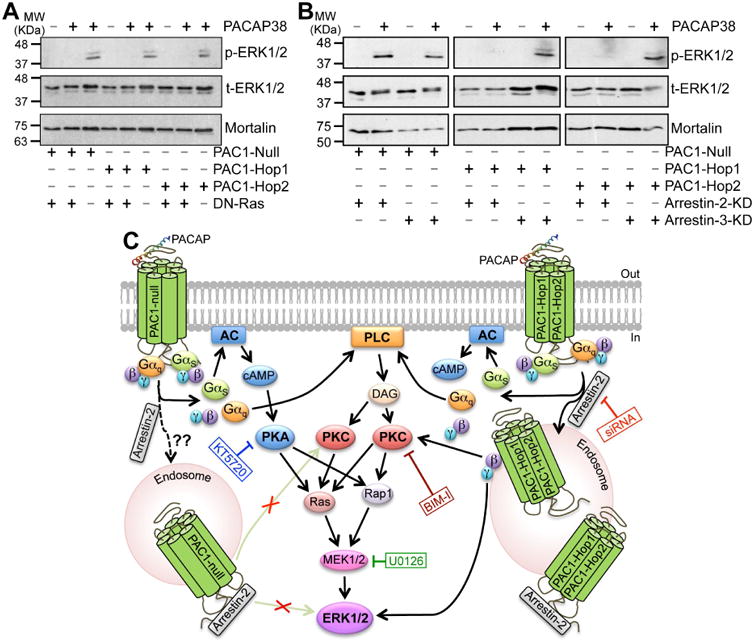
Ras and arrestin-2-dependence of PACAP38/PAC1-mediated ERK1/2 activation. A, representative immunoblots (from 3 independent experiments) of lysates obtained from HEK293T cells transfected with plasmid carrying YFP-tagged PAC1-Null, PAC1-Hop1 or PAC1-Hop2 cDNAs, with or without the plasmid carrying dominant-negative Ras, N17Ras (DN-Ras), as indicated below the blot panels. Lysates were collected from untreated cells, and from cells with PACAP38 treatment (100 nM; 20 min), as indicated on top of the blot panels. Numbers on the left denote the relative mobility of molecular weight markers. B, representative immunoblots (from 3 independent experiments) of lysates obtained from HEK293T cells stably expressing siRNA for arrestin-2 (arrestin-2-KD) or arrestin-3 (arrestin-2-KD), further transiently transfected with plasmid carrying YFP-tagged PAC1-Null, PAC1-Hop1 or PAC1-Hop2 cDNAs, as indicated below the blot panels. Lysates were collected from untreated cells, and from cells with PACAP38 treatment (100 nM; 20 min), as indicated on top of the blot panels. Numbers on the left denote the relative mobility of molecular weight markers. t-ERK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 denote total-ERK1/2 and phospho-ERK1/2, respectively, and the bottom row immunoblots show sample normalization for the same samples probed with anti-mortalin antibody for both panels a and b. PACAP38 treatment failed to induce any detectable ERK1/2 phosphorylation in DN-Ras transfected cells in all three PAC1 isoforms. Interestingly, PACAP38 treatment led to strong ERK1/2 phosphorylation in HEK293T cells stably expressing arrestin-3 siRNA with each individual PAC1 isoforms. However, PACAP38 treatment did not lead to any detectable ERK1/2 phosphorylation in cells stably expressing arrestin-2 siRNA with PAC1-Hop1 and Hop2, but not with the Null isoform. C, graphical scheme depicting the intracellular signaling cascades activated upon PACAP-stimulation of PAC1-Null or Hop1 or Hop2 receptors, as determined from results shown in Fig. 5B and 6A-C and 7A-B. Black arrows indicate stimulation/activation, and texts in blue, green, red and dark red boxes connected to blunt-ended lines indicate inhibition of specific signaling components with pharmacological modulators or dominant-negative overexpression or siRNA expression. Abbreviations for AC, cAMP, DAG, ERK1/2, MEK1/2, PLC, PKA and PKC are consistent with those described elsewhere in the manuscript.
