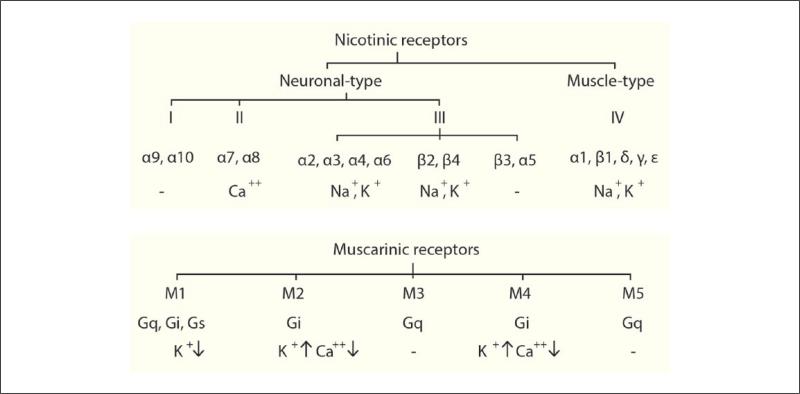
Figure 1.
Overview of cholinergic receptors with their functional effects. Nicotinic and muscarinic receptor trees. Nicotinic receptors (top) are divided into neuronal (I-III) and muscle (IV) types. Neuronal nAChRs are further subdivided into 3 subfamilies (I-III), with subfamily III further subdivided into three tribes. Subunits of nAChR assemble into homo- or hetero-pentamers to form an ionotropic receptor–channel complex. On activation, nAChRs mediate the influx of cations to depolarize the membrane and activate intracellular signaling. Muscarinic receptors (bottom) are encoded by five different genes, which translate into M1-M5 G-protein–coupled receptors. Upon binding to acetylcholine, these stimulate G-protein(s), which activates a cascade of chemical reactions, leading to changes in ion channel activity and synaptic transmission.