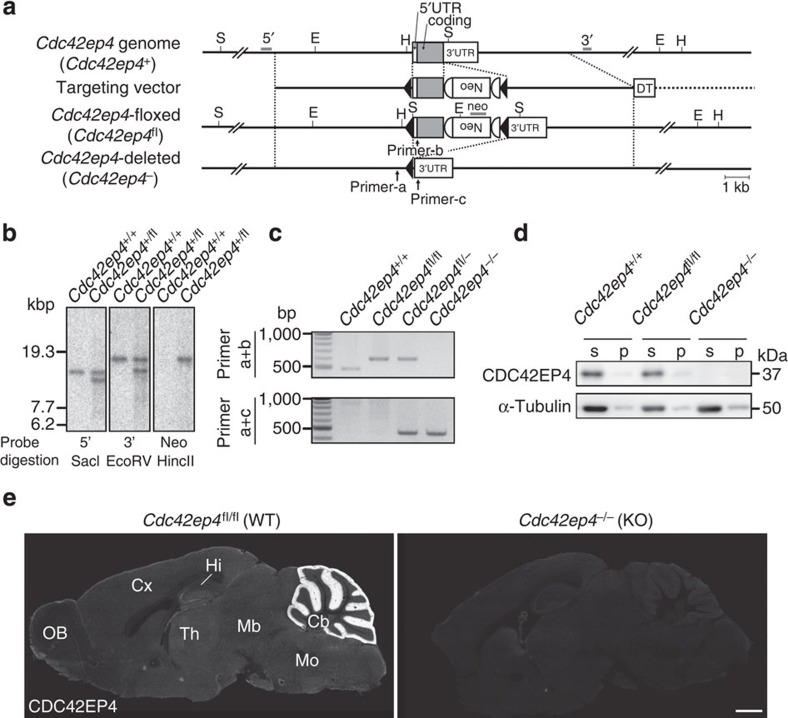
Figure 2. Generation of Cdc42ep4−/− mice and morphology of the major neuronal components.
(a) The KO strategy of the Cdc42ep4 gene. A schematic diagram showing the wild-type (Cdc42ep4+), floxed (Cdc42ep4fl) and null (Cdc42ep4−) alleles, and the targeting vector. Note that Cre-mediated loxP recombination leaves no coding exon. The restriction sites for Sac I (S), EcoR V (E) and Hinc II (H), three probes (grey bars) used for Southern blot analysis and three PCR primer sites are indicated. Signs; coding region (grey box), untranslated region (open box), loxP (black triangle), frt (open half-circle), neomycin resistance cassette (Neo), diphtheria toxin A-chain cassette (DT). (b) Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNAs purified from WT and the chimera (Cdc42ep4+/+;Cdc42ep4fl/+) mice were digested with the restriction enzymes and hybridized with the probes as indicated. The band patterns, as seen in preceding Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones, reconfirmed successful homologous recombination of the clone. See Methods for details. (c) PCR genotyping. Two sets of primers discriminated genomic DNAs from Cdc42ep4+/+, Cdc42ep4fl/fl (WT), Cdc42ep4fl/− and Cdc42ep4−/− (KO) mice. (d) Expression and extractability of CDC42EP4 in the adult mouse cerebellum. The pellet/supernatant assay showed that CDC42EP4 is partitioned mostly to the detergent-extractable, supernatant (s) fraction but not to the inextractable, pellet (p) fraction. CDC42EP4 was absent from KO tissues. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (e) IF for CDC42EP4 on parasagittal brain sections of adult male littermate WT and KO mice. The molecular layer of the WT cerebellum (Cb) was intensely labelled for CDC42EP4, which was absent from the KO brain. The faint, diffuse labelling of the entire brain is attributed to astrocytes. These results are consistent with the immunoblot data (Figs 1b and 2d) and warrant the specificity (high signal-to-noise ratio) of the antibody. Scale bar, 1 mm. UTR, untranslated repeat.