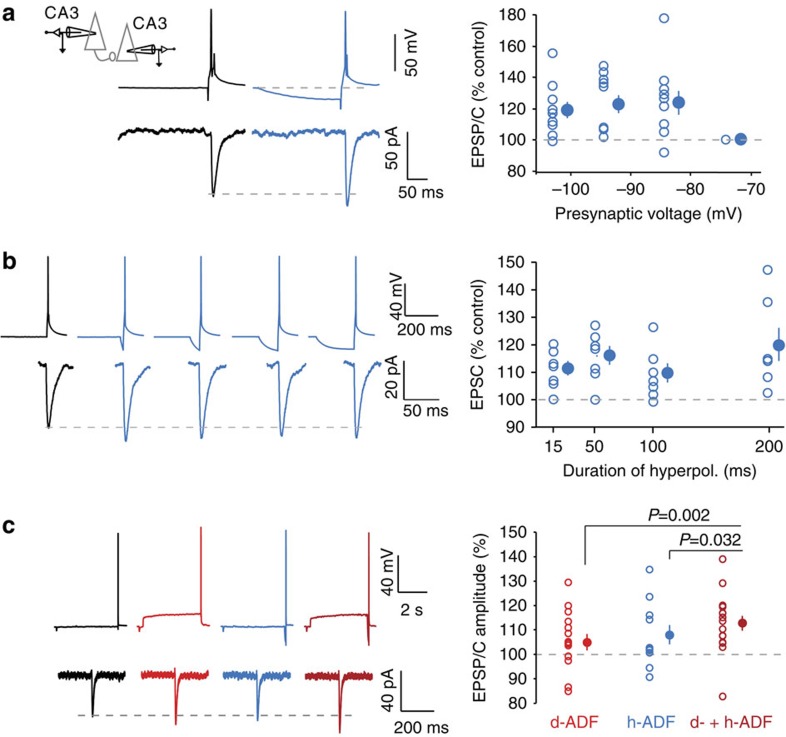
Figure 1. Synaptic facilitation induced by transient hyperpolarization (h-ADF) in CA3 neurons.
(a) Facilitation of synaptic transmission at CA3–CA3 connections by a hyperpolarizing pre-pulse (200 ms duration). Left, schematic of the recording configuration. Middle, example of facilitation produced by the presynaptic hyperpolarizing pulse (10 traces were averaged). Right, summary of facilitation induced by presynaptic hyperpolarization of increasing amplitude. Note that no further facilitation was induced when the magnitude of the hyperpolarizing pre-pulse was increased. (b) h-ADF can be induced by brief presynaptic hyperpolarization. Left, examples of recording from a pair of connected CA3 pyramidal neurons with no hyperpolarization and 15, 50, 100 and 200 ms of hyperpolarization to −93 mV before the spike. Right, summary of facilitation induced by 15, 50, 100 and 200 ms (all Wilcoxon test, P<0.05, n=7). (c) d- and h-ADF are coexpressed at CA3–CA3 connections. Left, representative example. Top traces, membrane potential of the presynaptic neuron in control (black), during d-ADF (red), during h-ADF (blue) and when d- and h-ADF are combined (dark red). Bottom traces, postsynaptic responses in each case averaged over 10 trials. Right, group data (Mann–Whitney test, n=16, for d-ADF, 11 for h-ADF and 16 for d- and h-ADF). Note the stepwise increase in transmission when d- and h-ADF are combined.