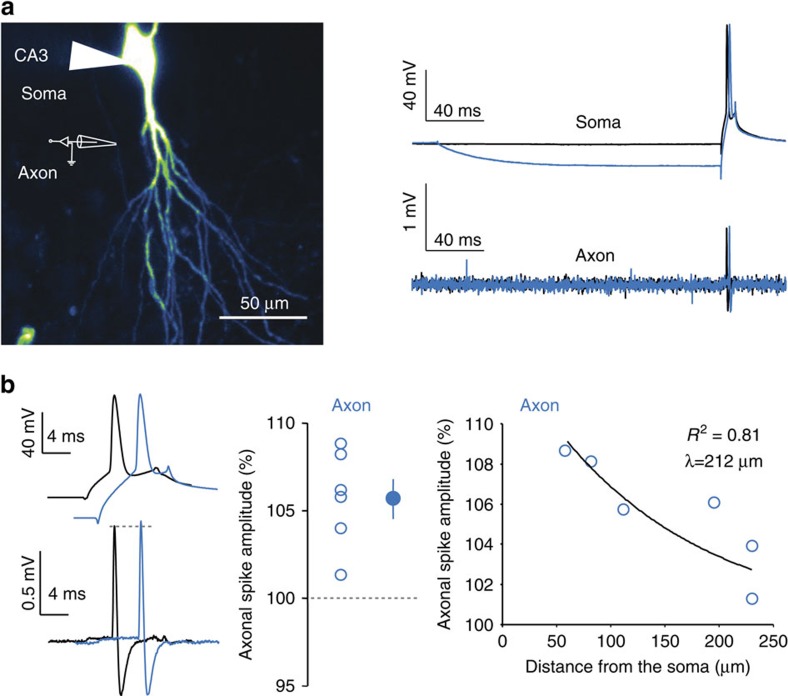
Figure 3. h-ADF enhances spike amplitude in the axon.
(a) Left, confocal image of a CA3 neuron filled with Alexa 488. The axon collateral (white arrow) is identified on the left and recorded in a cell-attached configuration. Right, simultaneous recordings from the soma (top) and axon (bottom) when the spike is triggered from resting membrane potential (black) or from a transient hyperpolarizing pre-pulse (blue). (b) Left, comparison of the spike amplitude measured in the axon evoked with (blue) or without (black) hyperpolarizing pre-pulse. Note the increase in amplitude in the axon when the spike is triggered from the hyperpolarizing pre-pulse. Middle, quantitative analysis of the hyperpolarization-induced enhancement of the axonal spike amplitude in six neurons. Right, scatter plot of the change in the axonal spike amplitude as a function of axonal distance (exponential fit, y=11.6e−x/212, r2=0.81).