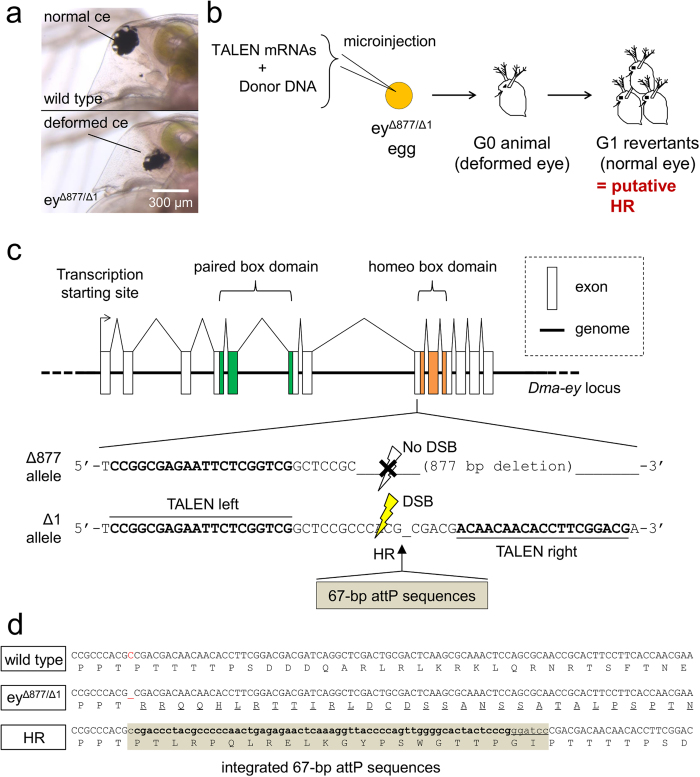
Figure 1. Strategy to induce TALEN-mediated HR in D. magna.
(a) Typical deformed eye phenotype of the eyΔ877/Δ1 strain. The top picture is derived from the wild type with a normal spherical compound eye (ce). The bottom picture is derived from the eyΔ877/Δ1 strain with deformed ce. Scale bar indicates 300 μm. (b) Overview of screening HR daphniids by phenotypic rescue. TALEN-mediated HR was induced by co-injection of TALEN mRNAs and donor DNA carrying exogenous DNA fragment into eggs from the eyΔ877/Δ1 strain. Because the integration of exogenous DNAs via HR was designed to result in recovering the frameshift mutation on the Δ1 allele in Dma-ey locus (see Fig. 1c,d), it was expected that the deformed eye phenotype would be rescued by germ line transmission of HR events. (c) Schematic gene structure of Dma-ey and partial sequences on the Δ877 allele and Δ1 allele. The Dma-ey gene putatively consists of 13 exons (shown by open boxes). DNA-binding domain-encoding regions are coloured in green (paired box) and orange (homeo box). The eyΔ877/Δ1 strain has 877 bp or 1 bp deletion mutations on respective alleles of the Dma-ey locus. TALEN-binding DNA sequences are highlighted in bold. TALEN proteins can induce double strand breaks (DSBs) only into the Δ1 allele because of the long deletion on the Δ877 allele, so that 67-bp attP would be integrated into the Δ1 allele via HR. (d) Comparison of putative genome sequences around the TALEN targeted sites among the wild type, eyΔ877/Δ1 strain, and HR revertant daphniids. Deduced amino acid sequences of each strain are described under the genome DNA sequence. The deleted base ‘C’ on the eyΔ877/Δ1 genome is highlighted in red. Altered Dma-EY peptide sequences are indicated by underline in eyΔ877/Δ1 strain. The entire integrated 67-bp fragment, which consists of 1 base of cytosine, 60 bases of attP (bold), and 6 bases of the BamHI recognition site (underline) is coloured beige.