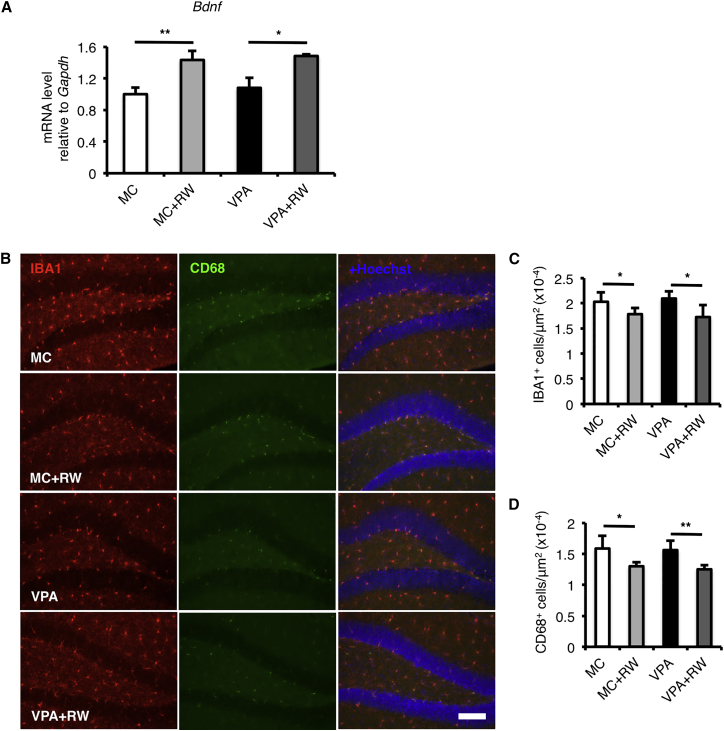
Figure 6.
Voluntary Running Increases the Bdnf Expression Level and Reduces Microglia and Activated Microglia in the Hippocampus
(A) The expression level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) was increased by voluntary running in both MC- and VPA-treated mice.
(B–D) Voluntary running reduced the number of IBA1+ microglia (red; B and C) and CD68+-activated microglia (green; B and D) in both MC- and VPA-treated mice.
MC, prenatal methylcellulose (vehicle); MC + RW, prenatal methylcellulose and postnatal running; VPA, prenatal valproic acid; VPA + RW, prenatal valproic acid and postnatal running; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Data are represented as means. n = 3 for each group. Error bars indicate the SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, two-tailed t test. Scale bar, 100 μm.