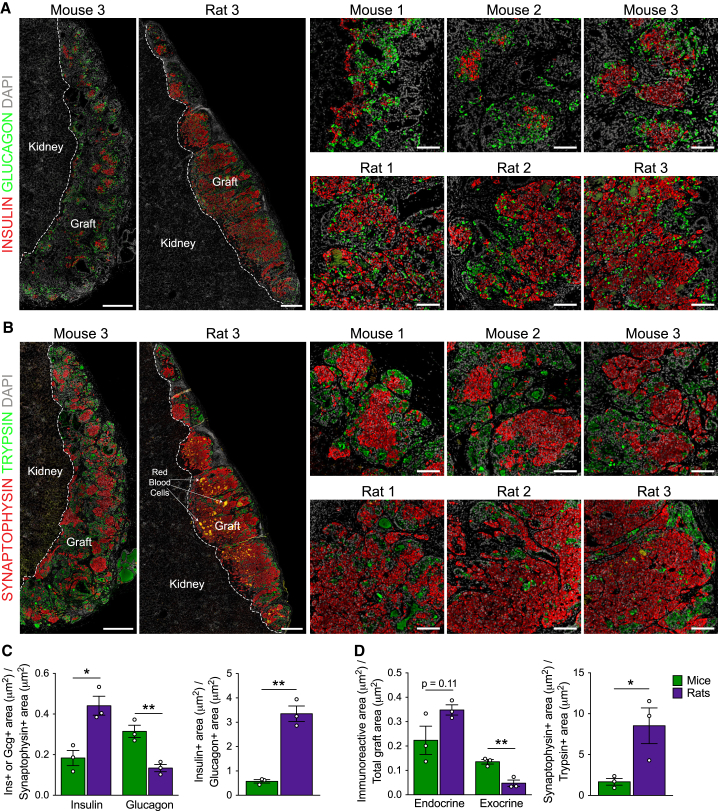
Figure 3.
Grafts from Rats Contained a Higher Proportion of Insulin:Glucagon and Synaptophysin:Trypsin Immunoreactivity Compared with Grafts from Mice
(A and B) Representative immunofluorescence images of whole hESC-derived grafts (graft and kidney tissue is delineated by a dashed white line; scale bars, 500 μm) and higher-magnification insets (scale bars, 100 μm) at 22 weeks post-transplantation. Shown are (A) insulin (red) and glucagon (green) and (B) synaptophysin (red, endocrine marker) and trypsin (green, exocrine marker). DAPI nuclear staining is shown in gray in all images.
(C) Area of insulin (ins) or glucagon (gcg) immunoreactivity relative to total synaptophysin immunoreactivity and insulin+ area relative to glucagon+ area for each graft.
(D) Area of synaptophysin or trypsin immunoreactivity relative to the total graft area and synaptophysin+ area relative to trypsin+ area for each graft.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; two-tailed t test. All data are presented as mean ± SEM plus individual biological replicates (n = 3 animals/group). See Figure S5 for additional immunofluorescent staining of hESC-derived grafts.