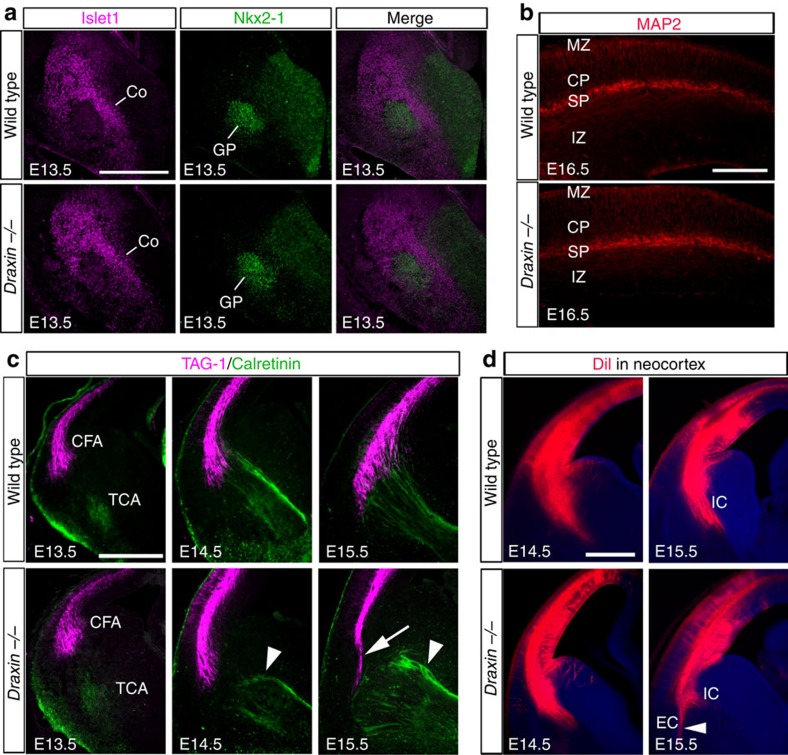
Figure 2. Aberrant thalamocortical projections precede aberrant corticofugal projections.
(a) Coronal sections from E13.5 brains of wild-type and draxin−/− mice stained with Islet1 and Nkx2-1 antibodies. The corridor and the globus pallidus cells were formed normally in draxin−/− mice (n=8 for each genotype). Scale bar, 500 μm. (b) Coronal sections from E16.5 brains of wild-type and draxin−/− mice stained with a MAP2 antibody. MAP2 expression was not affected in the neocortex of draxin−/− mice (n=8 for each genotype). Scale bar, 300 μm. (c) Coronal sections from E13.5–E15.5 brains of wild-type and draxin−/− mice stained with TAG-1 and calretinin antibodies. Arrowheads and the arrow indicate misprojected thalamocortical and corticofugal axons, respectively (n=8 for each genotype). Scale bar, 500 μm. (d) Coronal sections from E14.5 and E15.5 brains of wild-type and draxin−/− mice with a DiI injection in the neocortex. In draxin−/− mice, DiI-labelled axons from the neocortex correctly projected towards the internal capsule at E14.5, but some DiI-labelled axons misprojected towards the external capsule at E15.5 (arrowhead, n=5 for each genotype). Scale bar, 500 μm. CFA, corticofugal axons; Co, corridor cells; CP, cortical plate; GP, globus pallidus; IC, internal capsule; IZ, intermediate zone; MZ, marginal zone; SP, subplate; TCA, thalamocortical axons.