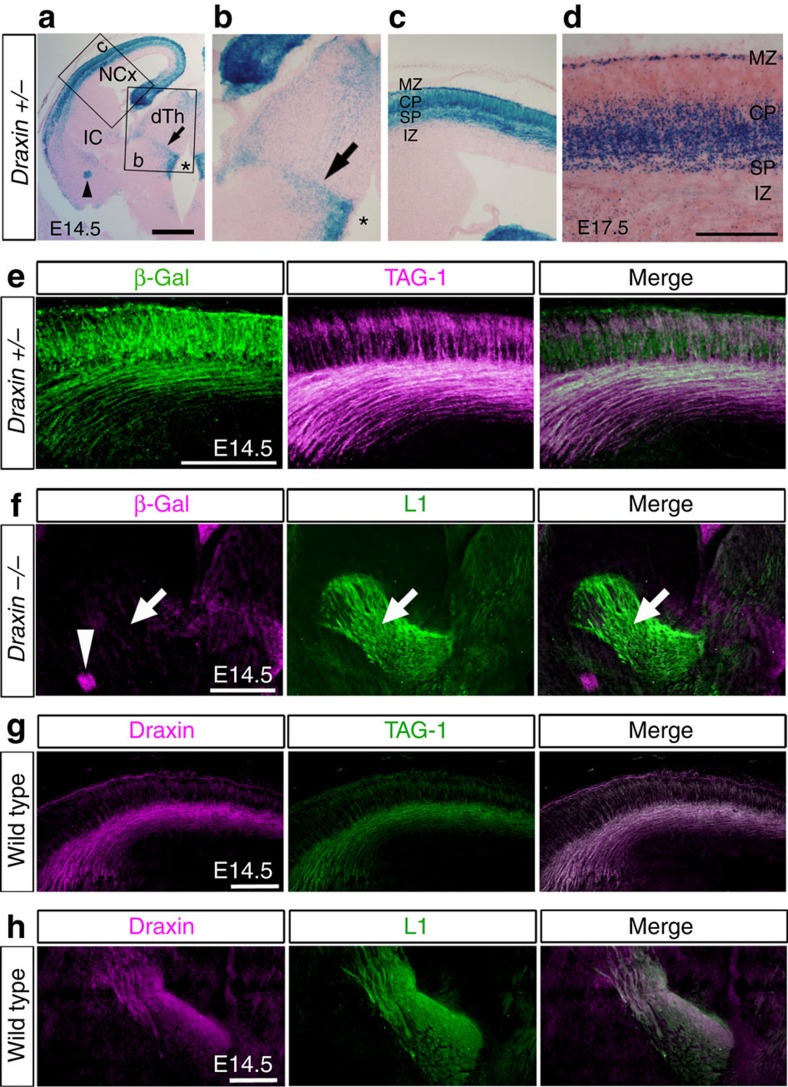
Figure 3. Draxin expression during corticofugal and thalamocortical development.
(a–c) draxin expression visualized with β-gal staining in coronal sections of E14.5 draxin+/− mice. draxin was strongly expressed in the neocortex and weakly expressed in the ventral telencephalon and the thalamus. Arrow, asterisk and arrowhead indicate draxin expression in the zona limitans intrathalamica, the ventricular zones of the ventral thalamus and a small portion of the amygdala, respectively. Scale bar, 500 μm. (d) draxin expression revealed with β-gal staining in the neocortex at E17.5. draxin expression was observed in early-born neurons, including in the subplate neurons. Scale bar, 200 μm. (e) Double immunostaining with β-gal and TAG-1 antibodies in draxin+/− mice revealed that neocortical neurons express draxin. Scale bar, 200 μm. (f) Double immunostaining with β-gal and L1 antibodies in draxin−/− mice. Even in draxin−/− mice that show strong β-gal expression compared with that in draxin+/− mice, β-gal expression was not visible in thalamocortical axons. Scale bar, 400 μm. (g,h) Double immunostaining with draxin/TAG-1 and draxin/L1 antibodies showed the presence of draxin proteins in the corticofugal and thalamocortical axons. Scale bars, 200 μm.