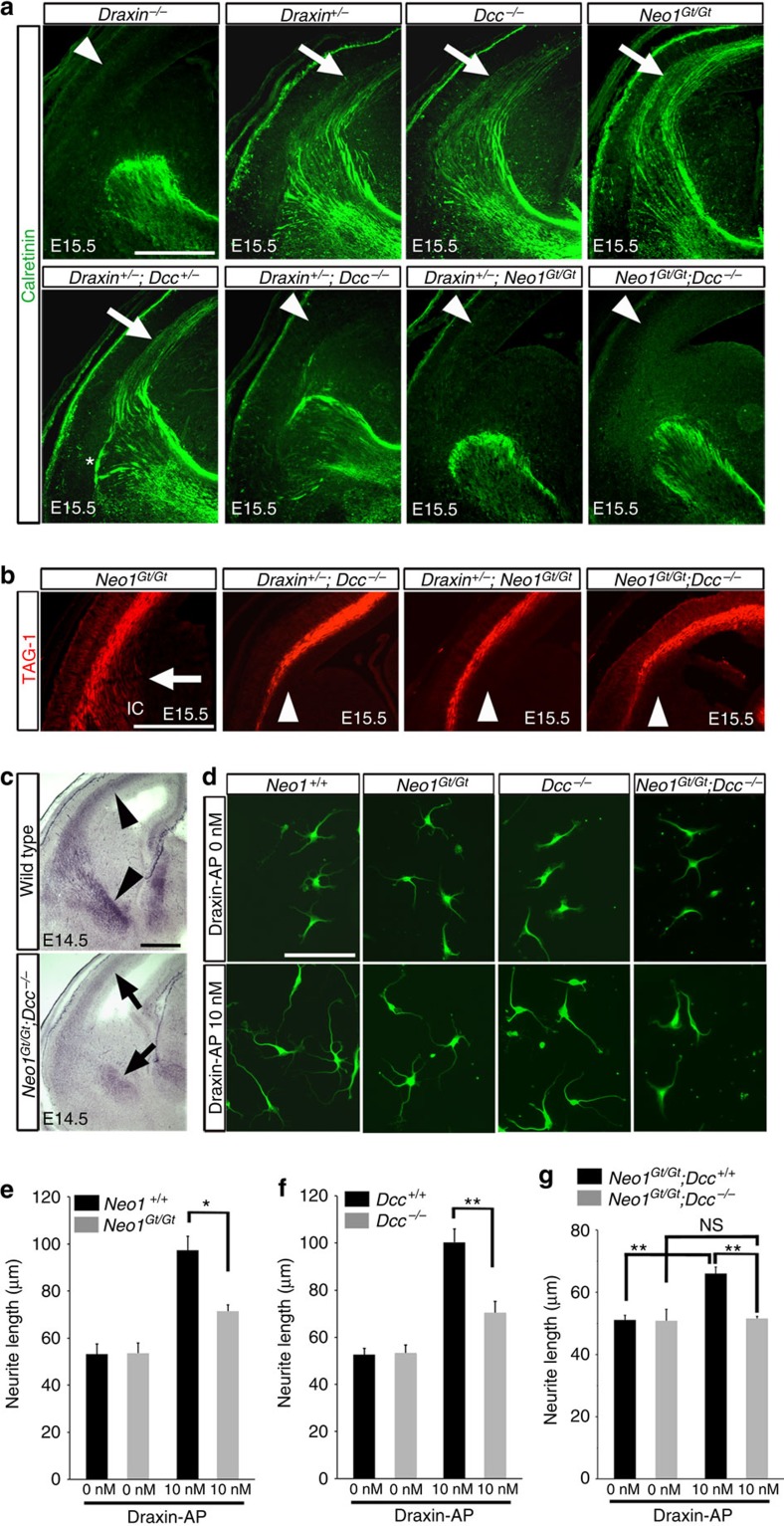
Figure 6. DCC and Neo1 are required for draxin receptor signalling.
(a) Coronal sections from E15.5 brains of draxin−/−, draxin+/−, Dcc−/−, Neo1Gt/Gt, draxin+/−;Dcc+/−, draxin+/−;Dcc−/−, draxin+/−;Neo1Gt/Gt and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice stained with a calretinin antibody. Thalamocortical projections into the neocortex were disrupted in draxin+/−;Dcc−/−, draxin+/−;Neo1Gt/Gt and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice (arrowheads), but were not affected in draxin+/−, Dcc−/− and Neo1Gt/Gt mice (arrows). An asterisk indicates the misrouted thalamocortical axons. Scale bar, 500 μm. (b) Coronal sections from E15.5 brains of Neo1Gt/Gt, draxin+/−;Dcc−/−, draxin+/−;Neo1Gt/Gt and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice stained with a TAG-1 antibody. TAG-1-positive axons of the Neo1Gt/Gt mice extended into the internal capsule (arrow). In contrast, TAG-1-positive axons of draxin+/−;Dcc−/−, draxin+/−;Neo1Gt/Gt and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice did not extend into the internal capsule (arrowheads, n=4 for each genotype). (c) Draxin-AP binding in coronal sections from E14.5 brains of wild-type and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice. Draxin-AP binding in the intermediate zone of the neocortex and the internal capsule in Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice (arrows) was weaker than that in wild-type mice (arrowheads, n=3 for each genotype). Scale bar, 500 μm. (d–g) Dissociated cultures of thalamic neurons from Dcc−/−, Neo1Gt/Gt and Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− mice showed that DCC and Neo1 are necessary for the outgrowth-promoting effects of draxin. Scale bar, 100 μm. Quantification of the neurite outgrowth in Neo1Gt/Gt (e) and Dcc−/− (f) neurons in the presence of draxin-AP proteins. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=4 independent experiments). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 by Welch's t-test. (g) Quantification of the neurite outgrowth in Neo1Gt/Gt;Dcc−/− neurons in the presence of draxin-AP proteins. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=4 independent experiments). **P<0.01 and NS (not significant) by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's honest significance test.