Figure 4.
Visualization of Intraarterial Injected Fluc-hNIS+ mMABs via Small-Animal PET
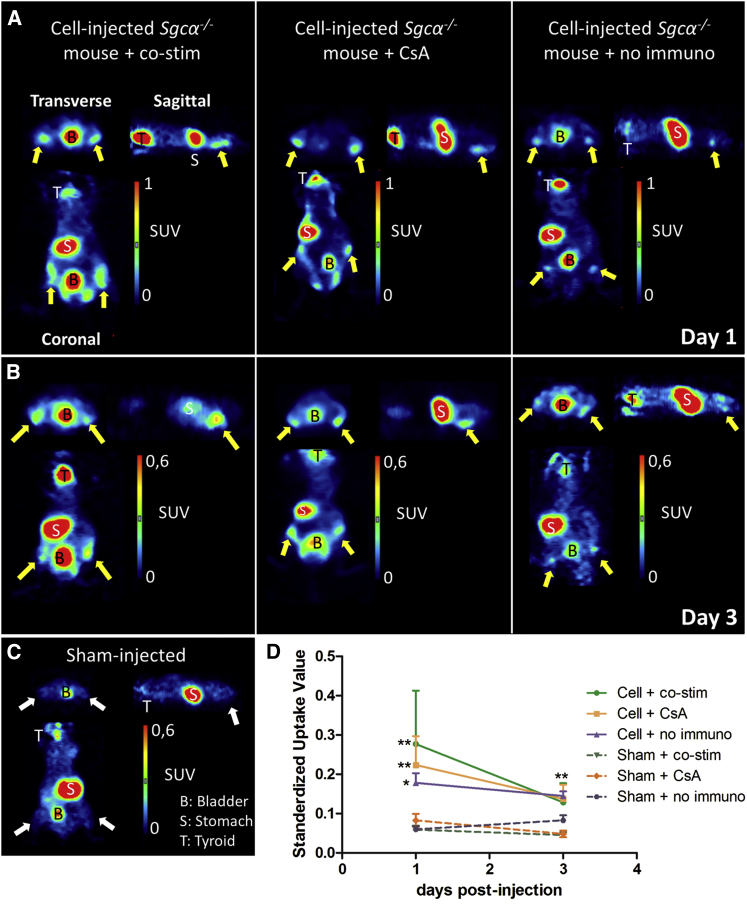
(A–C) 1 × 106 Fluc-hNIS+ mMABs were injected bilaterally in the femoral arteries of Sgca−/− mice (n = 4 IR) without immune suppression or with co-stim or CsA as immune suppression. Sham-injected animals were also included for all groups (n = 3 IR). At 1 and 3 days after cell injection, 124I− was administered. Clear tracer uptake could be observed in the hind limbs of cell-injected animals (indicated via the yellow arrows) at day 1 (A) and day 3 post-injection (B), which was absent in sham-injected animals (indicated via the white arrows) (C). The regions where NIS was endogenously expressed (thyroid, T, and stomach, S) also were clearly visible, together with the bladder.
(D) Quantitative analysis clearly demonstrated significantly higher SUVs in the hind limbs of cell-injected animals compared to sham-injected animals (∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05) without significant differences between the different cell-injected groups (mean ± SD).