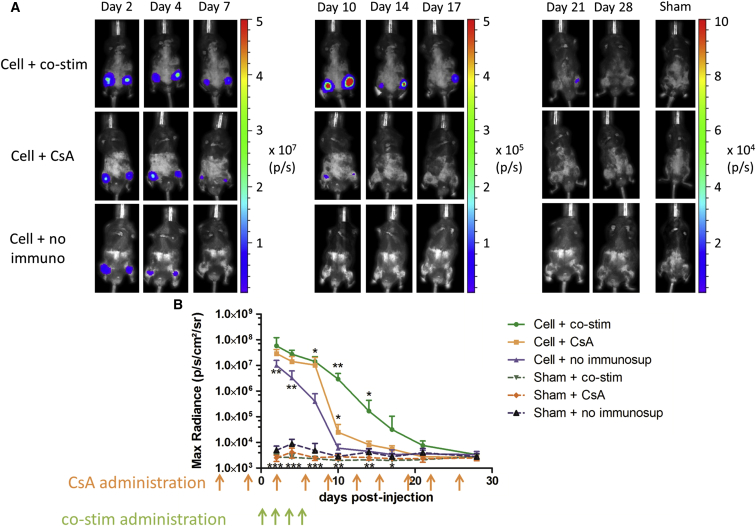
Figure 5.
Monitoring of Intraarterial Injected Fluc-hNIS+ mMABs via BLI
(A) 1 × 106 Fluc-hNIS+ mMABs were injected bilaterally in the femoral arteries of Sgca−/− mice without immune suppression (n = 5 IR) or with co-stim or CsA as immune suppression (n = 6 IR). Sham-injected animals were also included for all groups (n = 5 IR). Robust BLI signals were present in all cell-injected animals the first days after injection, while only background signal was observed in sham-injected animals.
(B) Quantitative analysis demonstrated that starting from day 7, significantly higher BLI signals were present in cell-injected animals receiving immune suppression compared to cell-injected animals not receiving immune suppression (∗p < 0.05). Starting from day 10 until day 14, significantly higher cell survival was shown in animals receiving co-stim compared to CsA as immune suppressant (∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05) (mean ± SD). Cells were lost in animals without immune suppression at 10 days post-injection, at day 14 post-injection in animals with CsA, and at day 28 for animals receiving co-stim (see also Figure S2).