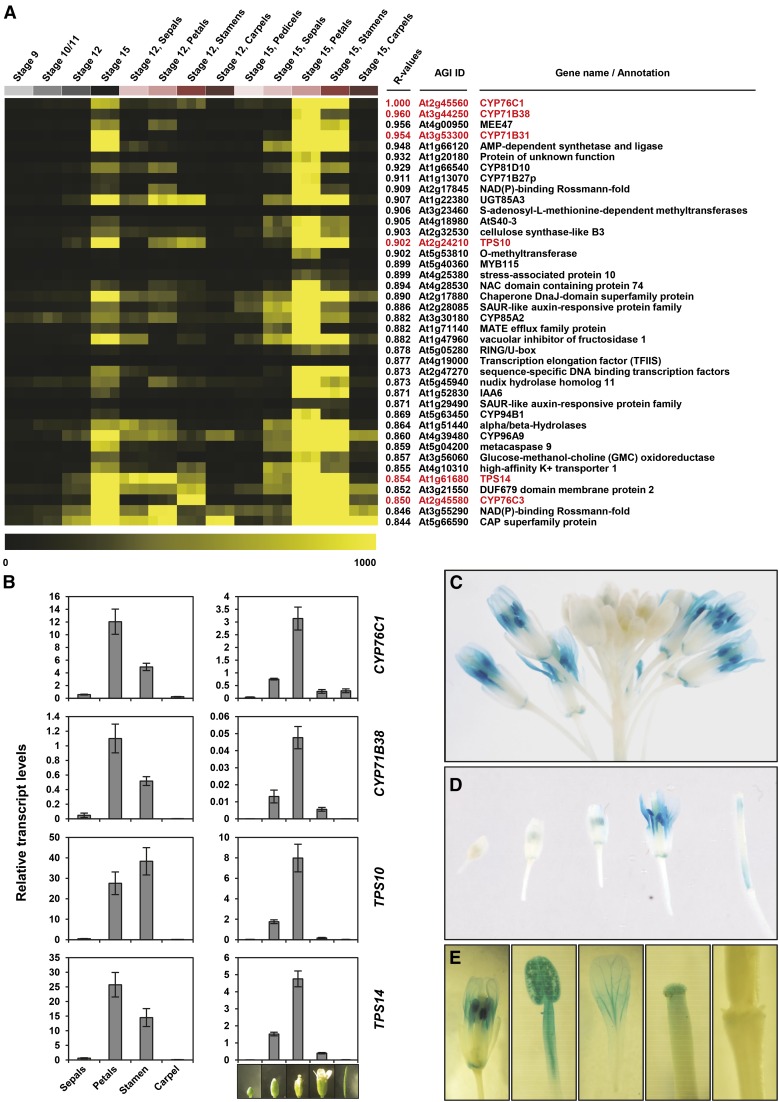
Figure 2.
CYP76C1 Expression and Coexpression Patterns in Arabidopsis Flowers.
(A) Expression heat map of the top 40 genes most closely coregulated with CYP76C1. Coexpression analysis was performed using the Expression Angler tool and the AtGenExpress Tissue Compendium data set (Toufighi et al., 2005). Heat map shows the expression levels in selected flowers tissues: flower stages 9, 10/11, 12, and 15 and petals, stamens, pedicels, and carpel at flower stages 12 and 15. Coexpressed genes are ranked according to their Pearson correlation coefficients with CYP76C1 (R values). Genes highlighted in red are known to be involved or putatively involved in linalool metabolism.
(B) Relative transcripts levels of CYP76C1, CYP71B38, TPS10, and TPS14 in flower organs (left panel) and during flower development (right panel). Relative transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR using the EΔCt method, and the specific efficiency of each primer pair and normalization with four reference genes for which the stable expression level are known (Czechowski et al., 2005). Results represent the mean ± se of three biological replicates for the flower parts and four biological replicates for flower stages.
(C) to (E) GUS staining showing spatiotemporal floral expression of CYP76C1. Staining was 19 h for inflorescence (C), flowers at different stages (D), and parts of fully opened flowers (E).