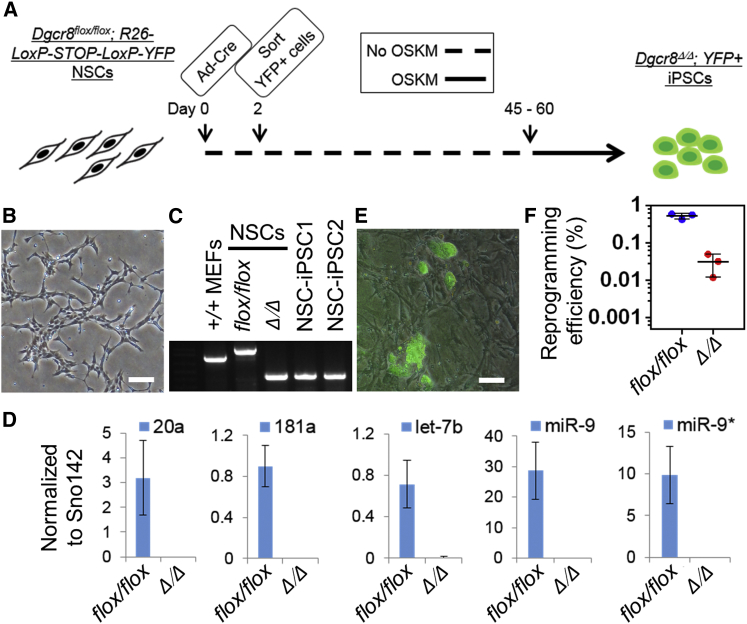
Figure 2.
Reprogramming of Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSCs
(A) Schematic of the reprogramming strategy. R26-loxP-STOP-loxP-YFP, ROSA26-driven loxP-flanked STOP sequence followed by an YFP reporter; Ad-Cre, Cre-expressing adenovirus; OSKM, reprogramming factors OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and c-MYC.
(B) Bright field image of Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSCs continuously cultured for 60 days. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(C) PCR genotyping of wild-type MEFs, Dgcr8flox/flox NSCs, Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSCs, and representative Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSC-derived iPSC clones. See also Figure S2.
(D) QPCR analyses of mature miRNAs in Dgcr8flox/flox and Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSCs. Expression of mature miRNA was normalized to small nucleolar RNA 142. n = 3 independent biological repeats. Error bar, SD.
(E) Merged bright field and YFP image of NSC-derived Dgcr8Δ/Δ iPSCs. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(F) Reprogramming efficiency of Dgcr8flox/flox and Dgcr8Δ/Δ NSCs. n = 3 independent biological repeats. Error bar, SD.