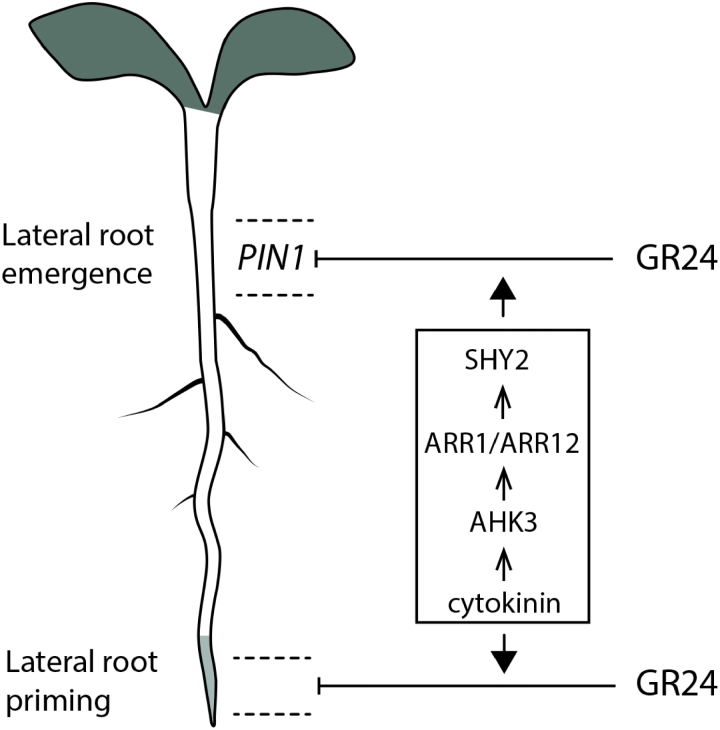
Fig. 5.
Working model on the interaction of cytokinins with the SL analog GR24 to control LR development. GR24 treatment results in inhibition of LR emergence, mainly, but not exclusively, near the root–shoot junction and, to a minor extent, in inhibition of LR priming in the root meristem zone. In the root region near the root–shoot junction, this LR emergence inhibition coincides with a spatial downregulation of PIN1 expression by GR24 treatment. The cytokinin module that signals via AHK3, through the response regulators ARR1/ARR12, and ultimately to SHY2, influences the effect of GR24 on LR development. Mutants in this pathway are insensitive to GR24, probably due to their reported increased PIN1 levels, because reduction of the auxin flux by NPA treatment renders the mutants sensitive again to GR24.