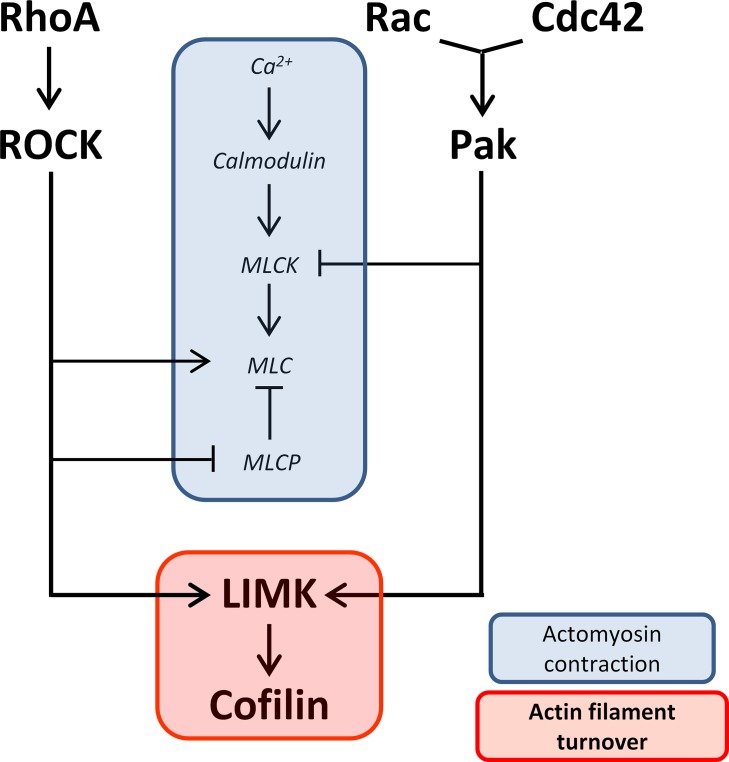
Figure 1.
Diagram of proposed pathways involved in rod cell axonal and neuritic plasticity. Two activities, actomyosin contraction and actin filament turnover, are suggested to contribute to plasticity in the axon and axon terminal after injury. Both RhoA-ROCK and Cdc42/Rac-Pak pathways converge on LIMK, which promotes actin filament turnover through regulation of cofilin. However, while RhoA-ROCK promotes actomyosin contraction through activating MLC and inhibiting MLCP, Cdc42/Rac-PAK inhibits it through inhibiting MLCK. Ca2+-calmodulin promotes actomyosin contraction through activating MLCK. RhoA, Rac, and Cdc42 are Rho GTPases; ROCK, Rho kinase; Pak, p21-activated kinase; LIMK, LIM kinase; MLC, myosin light chain; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase.