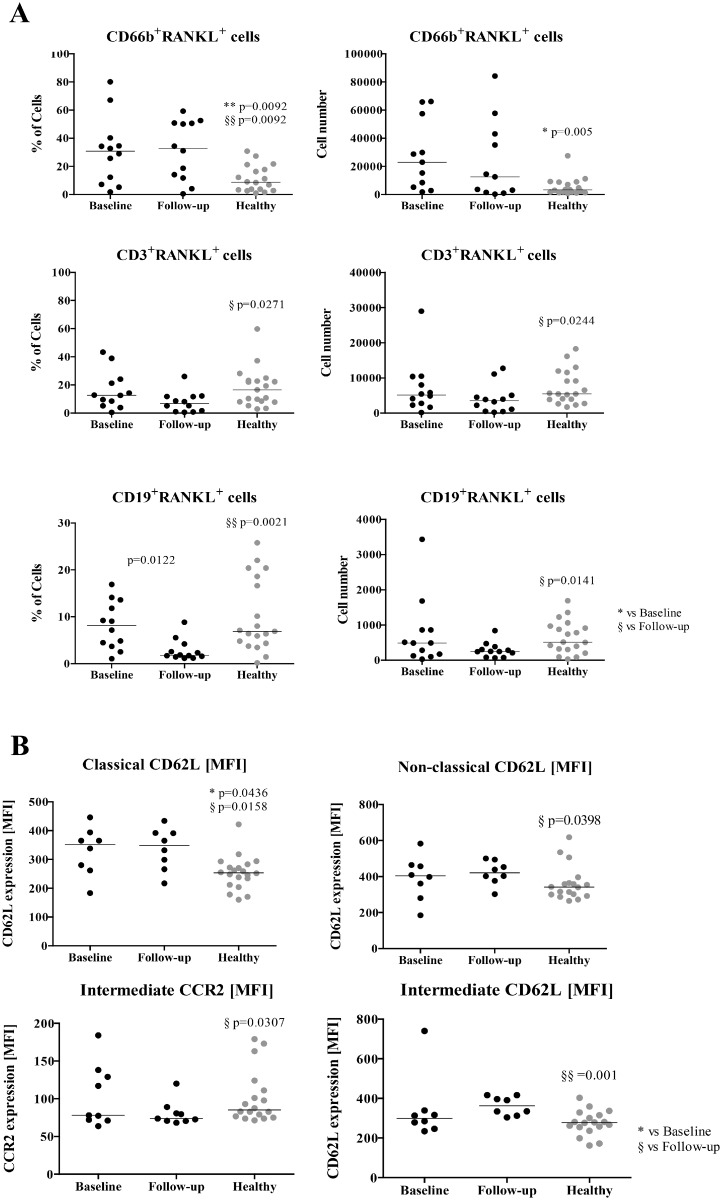
Fig 1. RANKL surface expression in leukocytes and monocyte phenotype.
A) RANKL+ frequency and absolute number in circulating leukocytes. CD66b+RANKL+ cells are increased in the circulation of patients at baseline and at follow-up when compared to healthy donors (frequency p = 0.0092; absolute number p = 0.005). At follow-up, CD3+RANKL+ are decreased in circulation when compared to healthy donors (frequency p = 0.0271; absolute number p = 0.0244). CD19+RANKL+ frequency is decreased after treatment when compared to patients at baseline (p = 0.0122) and with healthy donors (p = 0.0021). This difference is also observed at the absolute number level when compared to healthy donors (p = 0.0141). RANKL+ cells were analysed by flow cytometry and gated inside each subpopulation. B) Phenotype of circulating monocyte subpopulations—Classical CD14brightCD16-, intermediate CD14brightCD16+, non-classical CD14dimCD16+. CD62L is increased in the circulating classical subpopulation of patients at baseline (p = 0.0436) and at 6 months follow-up (p = 0.0158) when compared to healthy donors. CD62L expression is increased in patients after 6 months follow-up both in the non-classical subpopulation (compared to healthy p = 0.0398) and in the intermediate subpopulation (compared to healthy p = 0.001). CCR2 expression is reduced in the intermediate subpopulation of patients at follow-up when compared to healthy donors (p = 0.0307). Each dot represents a sample. Line represents median. * vs Baseline, § vs Follow-up. * and § p<0.05, ** and §§ p<0.01. MFI—Median fluorescence intensity.